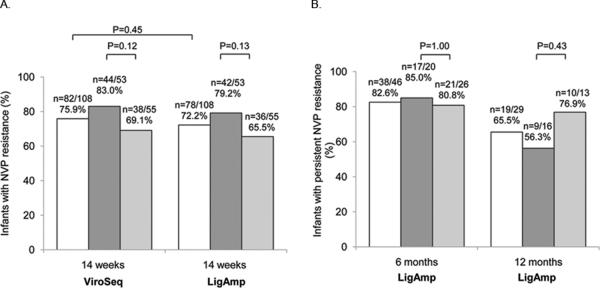
Figure 1.
Resistance test results are shown for all infants tested (no shading), infants in the extended NVP arm (dark shading), and infants in the extended NVP+ZDV arm (light shading). (A) Panel A shows results obtained for samples collected at 14 weeks of age using the ViroSeq assay (detection of any NVP resistance mutation) and the LigAmp assay (detection of K103N and/or Y181C). The proportion of infants with NVP resistance detected with ViroSeq vs. LigAmp at 14 weeks was compared using McNemar's test. The proportion of infants with NVP resistance at 14 weeks in the two study arms was compared using Fisher's exact test. In 10 infants, NVP resistance was detected with ViroSeq only. Five of the 10 infants had NVP resistance mutations that were not probed by the LigAmp assay (V106A, Y188C/L, G190A). In four of the 10 infants, K103N or Y181C was encoded by a codon that was not probed with the LigAmp assay (K103N was encoded by AAT rather than AAC, Y181C was encoded by TGC rather than TGT). In six infants, NVP resistance was detected by LigAmp only. In those cases, the level of the relevant mutation (K103N or Y181C) was <20% of the viral population. (B) Panel B shows results obtained for samples collected at 6 and 12 months of age using the LigAmp assay (detection of K103N and/or Y181C). Samples collected at 6 months of age were analyzed if the infant had K103N and/or Y181C detected at 14 weeks. Samples collected at 12 months of age were analyzed if the infant either had K103N and/or Y181C detected at 6 months of age, or had K103N and/or Y181C detected at 14 weeks of age and did not have a 6-month sample available for analysis. The proportions of infants with NVP resistance in the two study arms at 6 and 12 months were compared using Fisher's exact test.