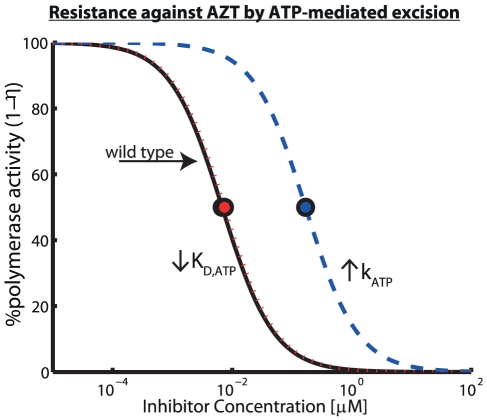
Figure 5. Molecular mechanisms of HIV-1 resistance development against AZT by ATP-mediated excision.
Potential mechanisms for resistance development against AZT through increasing its excision rate 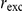 via an ATP-mediated mechanism (see eq. (21)). We calculated residual DNA-dependent polymerization of a Poly-T sequence in unstimulated
via an ATP-mediated mechanism (see eq. (21)). We calculated residual DNA-dependent polymerization of a Poly-T sequence in unstimulated  T-cells using eq. (19) with parameters from Tables 1, S1 and S3 (supplementary material). The solid black line shows residual DNA polymerization
T-cells using eq. (19) with parameters from Tables 1, S1 and S3 (supplementary material). The solid black line shows residual DNA polymerization  in the wild type virus, whereas the dotted red line and the dashed blue line refer to residual polymerization if
in the wild type virus, whereas the dotted red line and the dashed blue line refer to residual polymerization if 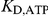 and
and 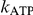 were decreased- and increased 100-fold respectively.
were decreased- and increased 100-fold respectively.