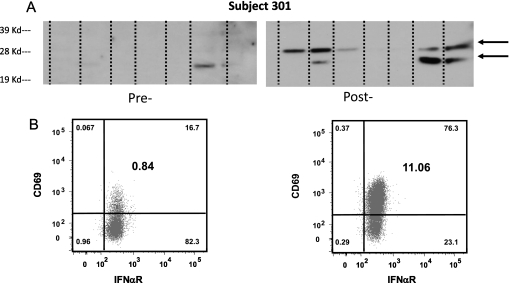
Figure 1.
Anti-tumor immune responses. (A) Anti-tumor humoral immune responses. Extracts from seven different mesothelioma cancer cell lines were run on an SDS-PAGE gel, transferred to nitrocellulose, and immunoblotted with diluted (1:1,500) pre- and 6-wk post-gene transfer serum from Subject 301. Note the presence of new bands at 25 and 30 kD (arrows) recognized by the post-gene transfer serum. (B) Activation of NK Cells. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from a pretreatment sample and a sample 2 days after gene transfer were studied from Subject 309 using flow cytometry. NK cells were identified on the basis of the cell surface expression of CD56 and CD16 after gating on the CD3-/CD14-/CD19-/CD20- lymphocytes. Shown are CD3-/CD14-/CD19-/CD20-/CD56dim/CD16+ cells expressing the activation marker CD69 and IFNαR, before gene transfer (A) and 2 days after gene transfer (B). Numbers in the smaller font in the corner of each quadrant represent % of each subset in the parent gate, while numbers in larger font in the middle of the right upper quadrant represent % of activated NK cells (CD3-/CD14-/CD19-/CD20-/CD56dim/CD16+/CD69+/IFNαR+) in the lymphocyte gate. Note the marked up-regulation of the activation marker CD69 in the post-treatment sample.