Figure 3. Effects of reducing agents and MTS reagents on the ability of SR-BI to mediate selective HDL-CE transport.
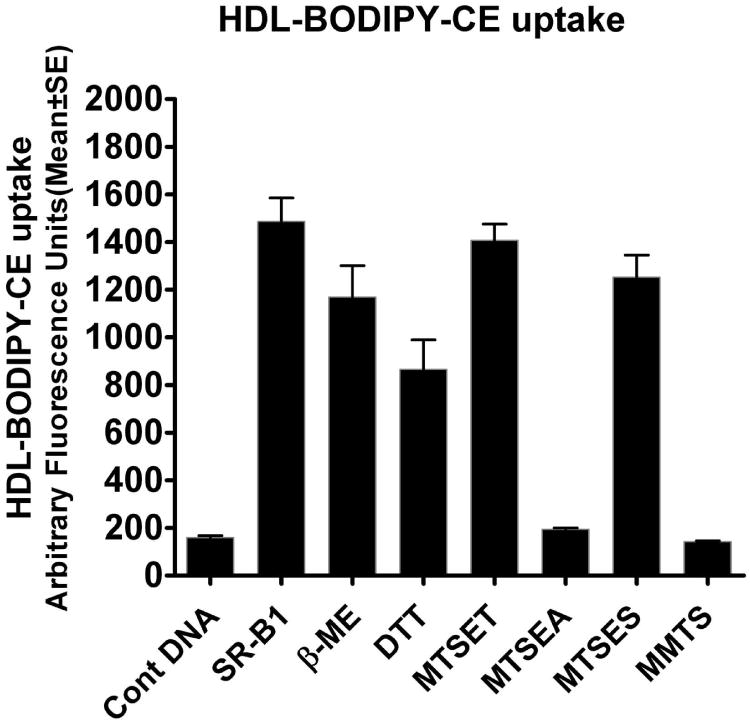
Intact COS-7 cells transiently expressing rat SR-BI were preincubated with freshly prepared DTT (10 mM) or β-mercaptoethanol (100 mM) at 37°C for 30 min. Likewise, some SR-BI overexpressing COS-7 cell dishes were pre-treated with freshly prepared MTSEA, MTSET, MTSES or MMTS (1 mM) for 5 min. After a few washes, the intact cells were then incubated for 5 min at 37°C with HDL-BODIPY-CE, and selective HDL-BODIPY-CE uptake by the COS-7 cells was quantified by the fluorescence measurement as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Each bar represents the Mean ± SE of data obtained from at least three independent experiments. As can be seen no significant change in HDL-BODIPY-CE uptake was observed when SR-BI expressing COS-7 cells were treated with disulfide (S-S) bond reducing agent β-mercaptoethanol or DTT. In contrast, treatment of SR-BI expressing cells with cysteine (SH) reactive alkyl methanethiosulfonate (MTS) reagents, MTSEA, MTSET and MMTS completely blocked the SR-BI-mediated selective HDL-BODIPY-CE uptake, whereas cells were relatively insensitive to treatment with the negatively charged MTSES. SR-BI-V5 alone vs + β-mercaptoethanol (β-ME), p = 0.00715; SR-BI-V5 alone vs + dithiothreito (DTT), p = 0.00458; SR-BI-V5 alone vs + MTSEA, p = 0.00017; SR-BI-V5 alone vs + MTSES, p = 0.08908 (NS); SR-BI-V5 alone vs + MMTS, p = 0.0.00014; SR-BI-V5 alone vs + MTSET p = 0.316155 (NS).
