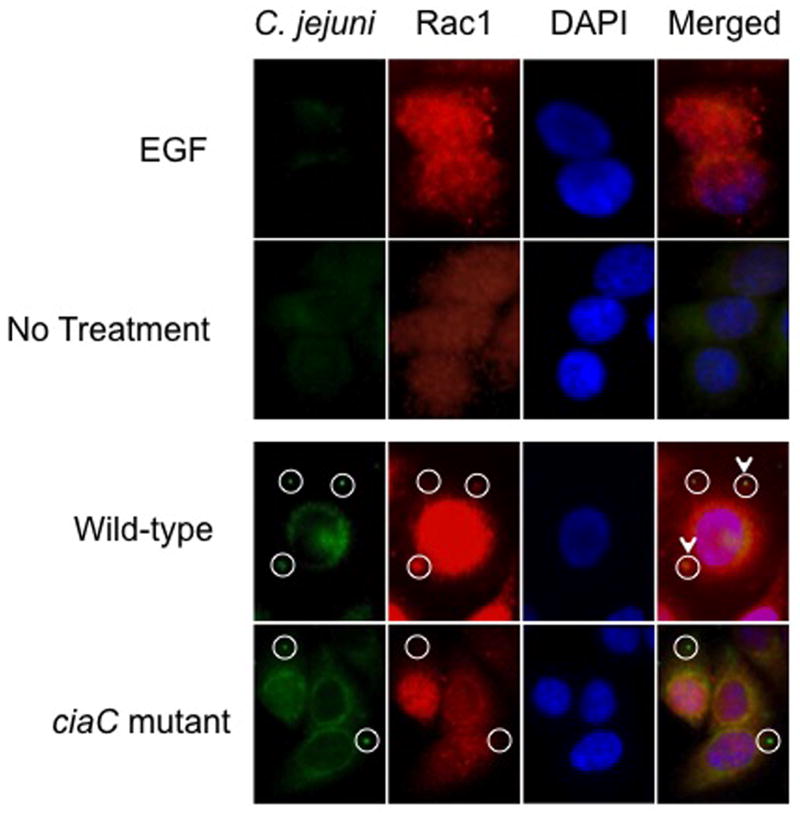
Fig. 4.
Rac1 is recruited to sites of C. jejuni attachment. The localization of Rac1 in C. jejuni-infected cells was examined by immunofluorescence microscopy as outlined in “Experimental Procedures.” EGF-treated cells served as a positive control and uninoculated (non-EGF treated) INT 407 cells were used as a negative control. EGF treatment of INT 407 cells resulted in Rac1 enriched sites, whereas Rac1 was dispersed in uninoculated INT 407 cells. The cell-associated bacteria are indicated by the circles, whereas the C. jejuni adjacent to sites of accumulated Rac1 are indicated by the circles with the arrowhead. Approximately 33% of the C. jejuni wild-type bacteria were co-localized with Rac1, whereas only 13% of the C. jejuni ciaC mutant bacteria were co-localized with Rac1.