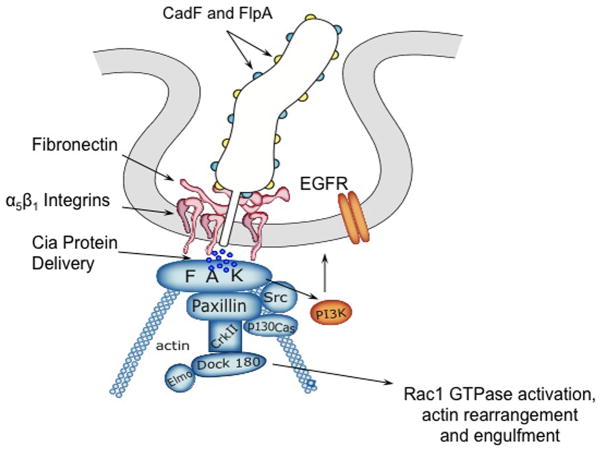
Fig. 8.
Model of the host cell EGF signaling pathway and proteins downstream of the EGF receptor that are activated in response to C. jejuni invasion. Indicated in blue are components of the focal complex, (FC) and indicated in orange are other components that likely participate in C. jejuni internalization. C. jejuni binding to Fn results in integrin occupancy and clustering, which in turn, leads to integrin activation. The activation of EGFR and FAK then occurs through from the association with the tails of clustered β1 integrins. Activated FAK autophosphorylates Tyr397, resulting in association of c-Src. c-Src phosphorylates additional residues within FAK as well as other members of the FC, including paxillin and p130Cas. This activation results in the recruitment of CrkII and Dock180, the latter of which associates with ELMO to expose its catalytic domain. The Dock180/ELMO complex activates the Rho family monomeric G protein Rac1, leading to a local restructuring of the actin cytoskeleton.