Figure 1.
RPAP2 Exists in Two Distinct Complexes
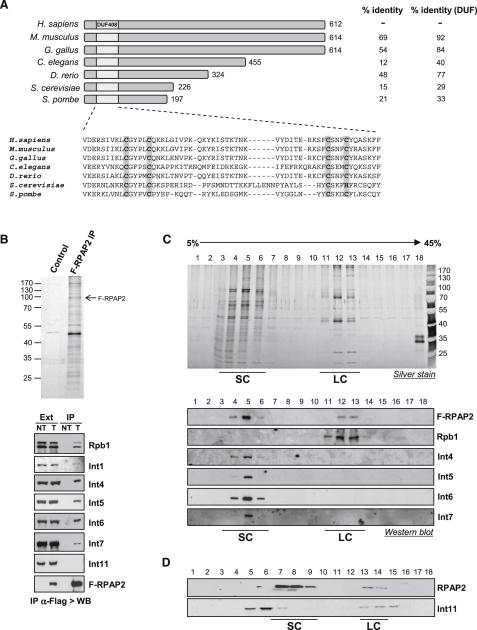
(A) Homologs of RPAP2 from the indicated species are shown on the diagram. Percent identity with RPAP2 and the DUF408 domain is indicated at the right. The DUF408 domain sequence was aligned to its mouse (M. musculus, NP_659160), chicken (G. gallus, XP_422341), C. elegans (CAA78048), zebrafish (D. rerio, AAH95735), S. cerevisiae (P40084), and S. pombe (NP_594445) homologs. Conserved cysteine residues are highlighted.
(B) SDS gel showing RPAP2 affinity eluate prepared from F-RPAP2-transfected cells. Nontransfected HeLa cells were used as a control for the Flag purification. Western blots are shown confirming the presence of Rpb1, Int1, Int4, Int5, Int6, Int7, and F-RPAP2 but not Int11 in the eluate.
(C) Fractionation of the F-RPAP2 eluate by ultracentrifugation on a glycerol gradient. Distribution of F-RPAP2, Rpb1, Int4, Int5, Int6, and Int7 in the gradient fractions was monitored by western blot using antibodies to the proteins noted at the right. SC, small complexes; LC, large complexes.
(D) Fractionation of HeLa cell extract on glycerol gradient. Distribution of endogenous RPAP2 and Int11 was monitored by western blot.
See also Figure S1.