Abstract
The human cathelicidin antimicrobial protein hCAP18, which includes the C-terminal peptide LL-37, is a multifunctional protein. As a possible approach to enhancing the resistance to plant disease, a DNA fragment coding for hCAP18/LL-37 was fused at the C-terminal end of the leader sequence of endopolygalacturonase-inhibiting protein under the control of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter region. The construct was then introduced into Brassica rapa. LL-37 expression was confirmed in transgenic plants by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and western blot analysis. Transgenic plants exhibited varying levels of resistance to bacterial and fungal pathogens. The average size of disease lesions in the transgenic plants was reduced to less than half of that in wild-type plants. Our results suggest that the antimicrobial LL-37 peptide is involved in wide-spectrum resistance to bacterial and fungal pathogen infection.
Keywords: Antimicrobial peptide, Cathelicidin, Disease resistance, Transgenic Chinese cabbage
Introduction
Bacterial and fungal plant pathogens severely affect crop productivity. For example, Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris and Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum, which cause black rot and soft rot, respectively, are present worldwide and severely damage plants and reduce their yields, especially in cruciferous plants (Boman 2003). Therefore, the development of cruciferous plants that are resistant to black and soft rot diseases has been a major goal of researchers for several decades. Strategies based on transgenic approaches to enhance plant disease resistance involve the use of genes associated with plant defense pathways (Makandar et al. 2006; Zhang et al. 2007) and genes encoding plant or fungal hydrolytic enzymes (Bieri et al. 2003), defense-related transcription factors (Chen and Chen 2002; Sohn et al. 2006) and antimicrobial peptides (Alan et al. 2004).
A large number of antimicrobial peptides from different organisms have been characterized (Simmaco et al. 1998). The human cathelicidin antimicrobial protein hCAP18 is the only member of the mammalian cathelicidin family of proteins that is present in humans (Gudmundsson et al. 1996). The holoprotein consists of a conserved prodomain, a cathelin domain, and the non-conserved C-terminal peptide LL-37, which is enzymatically cleaved after secretion (Sorensen et al. 2001; Yamasaki et al. 2006). Its precursor molecule, an 18 kDa human cationic antimicrobial protein (hCAP-18), is secreted by activated neutrophil granulocytes. After release, the helical C-terminal end of this precursor comprising 37 amino acids is cleaved off, thereby forming the functional antimicrobial peptide LL-37 (Sorensen et al. 2001). Since LL-37 is the only human antimicrobial peptide that is active at physiological or elevated salt concentration conditions, there is a significant interest in using this peptide for pharmaceutical applications (De Smet and Contreras 2005; Reddy et al. 2004; Travis et al. 2000).
In the present study, we report the transgenic expression of human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide carrying the substitution Met37Leu in Chinese cabbage. The expression of this peptide in cabbage plants significantly inhibited the growth of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum on the plant leaves, and it conferred resistance to several fungal pathogens. These results further support the assignment of a defense role to LL-37 and highlight its plant biotechnological potential.
Materials and methods
Expression vector construction
The leader sequence of the gene encoding Phaseolus vulgaris endopolygalacturonase-inhibiting protein (PGIP) (GenBank Accession No. X64769) was fused upstream of an LL-37-coding DNA fragment to cause the extracellular localization of the mature protein. The PGIP signal peptide (87 bp) was amplified by PCR with primers A linked with BamHI site (5′-CCGGATCCATGACTCAATTCAATATCCCA-3′) and B (5′-AGAGAGTGCAGTTCTCAA-3′). The coding region of LL-37 (111 bp) was substituted with Met-LL37-Leu and amplified by PCR from pFALL37 DNA using primers C (5′-ATGCTGCTGGGTGATTTCTTC-3′) and D with SacI site (5′-CGAGAGCTCCTAGGACTCTGTCC TGGG-3′). The two products were ligated into pBlueScript-SK (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA, USA) at the BamHI and SacI restriction sites. The generated LL-37 fragment was further amplified using primers A and D. For Agrobacterium transformation, the PCR product was subcloned into pBI121 binary vector driven by cauliflower mosaic virus 35S (CaMV35S) promoter (Gelvin 1998). The Ti plasmid vector construct pBI–LL37 was confirmed by DNA sequencing (ABI 377 DNA sequencer; Perkin-Elmer, Cypress, CA, USA).
Plant transformation and regeneration
The prepared construct was transformed into Chinese cabbage using the protocol described in Min et al. (2007). A total of 168 hypocotyls from in vitro grown seedlings of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa cv. Osome) were inoculated with Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain LBA4404 carrying either pBI-LL37 or pBI121. Green shoots that developed in the selective medium were transferred to a rooting medium containing 100 mg L−1 kanamycin and 500 mg L−1 carbenicillin. Rooted shoots were screened by PCR for the presence of the transgene before transfer to plastic pots.
Estimation of transformants and generation of homozygous lines
Self-pollinated seeds obtained from T0 plants were sown into plastic pots in the greenhouse. Two weeks after germination, seedlings were sprayed with 400 mg L−1 kanamycin in water; they were sprayed again 2 days later. Three days after the second spray, the ratios of green seedlings to bleached seedlings were determined, and the results were analyzed by a Chi-square test for goodness of fit to the ratios 3:1, 15:1, or 63:1. In order to obtain transformants homozygous for the LL-37 gene, kanamycin-resistant T1 progenies were grown to produce selfed T2 seeds. T2 lines that had no bleached segregants after kanamycin sprays were assumed to be homozygous for the LL-37 and nptII genes.
Molecular analysis of transformants
PCR analyses were conducted to detect the presence of LL-37- or nptII-specific fragments. Primers 35SF (5′-TCCACTGACGTAAGGGATGA-3′) and LL-37R (5′-CGAGAGCTCCTAGGACTCTGTCCTGGG-3′), which amplified a fragment of size approximately 750 bp, including sequences from the 3′ end of the 35S promoter, signal peptide (SP), and part of the LL-37 gene, were used to screen for putative LL-37 transformants. Putative transformants were screened using primers nptIIF (5′-TCGGCTATGACTGGGCACAACAGC-3′) and nptIIR (5′-AAGA AGGCGATAGAAGGCGATGCG-3′), which amplified a 722-bp nptII-specific fragment. Genomic DNA was isolated from young leaves of Chinese cabbage plants using a DNeasy Plant kit (Qiagen, Germantown, MD, USA.) as per the manufacturer’s instructions. PCR was performed and the reaction conditions were followed (1 cycle of 94°C for 1 min; 30 cycles of 94°C for 30 s, 55°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 1 min; and 1 cycle of 72°C for 10 min). The reaction products were electrophoresed on a 2% (w/v) agarose gel with 1× TAE buffer and visualized by staining with ethidium bromide.
In order to analyze gene expression in transgenic plants by RT-PCR, total RNA from wild-type and transgenic plants was reverse transcribed using AMV reverse transcriptase (Roche, USA) with oligo (dT) primers for 1 h at 42°C. The expression level of actin mRNA was used as a quantitative control.
Western blot analysis was performed by following standard molecular techniques (Sambrook et al. 1998). Briefly, for western blotting, 200 ng of purified protein or synthetic peptide was electroblotted onto a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane. Blots were probed with 1:1,000 dilution of polyclonal Hbt Ab antiserum raised in rabbit and then with 1:10,000 dilution of goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulin-peroxidase conjugate (Vector, Burlingame, CA, USA). The blots were then developed using the enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) developing system (GE Health Care, USA). The Low Range BioRad 161-0304 markers (BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA) were used as the molecular size markers.
Pathogen inoculation
P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum KACC 10057 obtained from the Korean Agricultural Culture Collection (http://kacc.rda.go.kr) was grown in Luria–Bertani (LB) medium until the absorbance at 600 nm (A 600) was 0.2, which corresponds to a concentration of approximately 2 × 108 CFU/mL. Three different concentrations of the culture (104, 106, and 108 CFU/mL) with 10 mM MgCl2 were inoculated by syringe infiltration. The inoculated plants were transferred to a growth chamber and incubated at 28°C under continuous light. They were examined for 12–96 h after inoculation. Lesion length (cm) and disease index (DI) were recorded for each individual plant; the disease index ranged from 0 to 6 on the basis of the development of the disease lesions: 0, no lesion; 1, lesion size 0.1–0.5 cm; 2, 0.5–1.5 cm; 3, 1.5–3.5 cm; 4, 3.5–5.5 cm; 5, 5.5–8.5 cm; and 6, over 8.5 cm or plant dead.
The fungi Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Lycopersici (KACC 40032), Colletotrichum higginsianum (KACC 40807), and Rhizoctonia solani (KACC 40107) were inoculated on plant leaves by placing 10 μl of an aqueous suspension containing 106 spores/mL on the leaves. Plants were maintained in highly humidified conditions (100% RH) at 25°C with 16 h of light in a growth chamber.
Evaluation of in vitro inhibition assays
Total and extracellular fluids were extracted by the methods described in Alan et al. (2004). Protein concentrations in the leaflet fluids were determined by the Bradford assay (Bradford 1976). The in vitro inhibition assays were evaluated by the protocol from Alan et al. (2004). Briefly, the experiments tested whether total fluid (TF) and extracellular fluid (EF) from three homozygous lines possessed antimicrobial activity. Assays were also performed using TF and EF from wild-type plant and LB medium as controls. A volume of 248 μL of TF, EF, and LB was mixed with 2.5 μL of 108 CFU/mL P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum in Eppendorf tubes and incubated on a shaker for 4 h. The samples remaining in the tubes were mixed in the ratio 1:9 with LB, returned to the shaker, and incubated overnight at 37°C. The bacterial growth in these tubes was determined by a spectrophotometer at 600 nm.
Results
Generation and characterization of LL-37 transgenic plants
The sequence of mature peptide of Met-LL37-Leu (GenBank accession No. NM-004345) is shown in Fig. 1a and the construct of binary pBI121 in Fig. 1b. Morphological characteristics of non-transformed Chinese cabbage (wt) and transgenic plants are shown in Fig. 1c. Transformation experiments with Agrobacterium carrying pBI-LL37 yielded 17 independent kanamycin-resistant putative transformants. Three out of 17 transformants showed abnormal phenotypes and eliminated for further experiment. PCR analysis with 35SF and LL-37R primers revealed that 11 of 14 transformants contained the expected amplified product (Fig. 2a). The PCR-positive plants (T0) were transferred to the greenhouse where they were further observed for their phenotypic characters and were grown for recovery of self-pollinated seeds. Most transformants were phenotypically similar to non-transformed plants. Segregation analysis was indicated that T1 transformants with a single copy showed 3:1 kanamycin resistance. Four of them were randomly selected for selfing, and named lines B11, B12, B13, and B14 (T2). Ten plants per line after selfing were screened on kanamycin to get homozygotics (T3). Additionally, we confirmed the integration of the genes in four homozygous lines (T3; B21, 22, 23, and 24 from T2; B11, 12, 13, and 14) by PCR using the 35S-specific, nptII-specific, and LL-37-specific primer sets (Fig. 2b). All of these contained the expected amplified product.
Fig. 1.
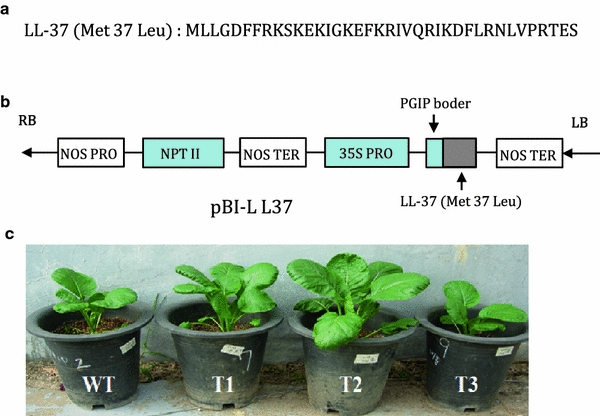
Construction of a binary plant expression vector pBI121 for the transformation of Chinese cabbage plants. a Sequence of the peptide (GenBank Accession No. NM-004345). b Schematic diagram of the expression construct pBI-LL37. c Morphological characteristics of non-transformed Chinese cabbage (wt) and transgenic plants
Fig. 2.
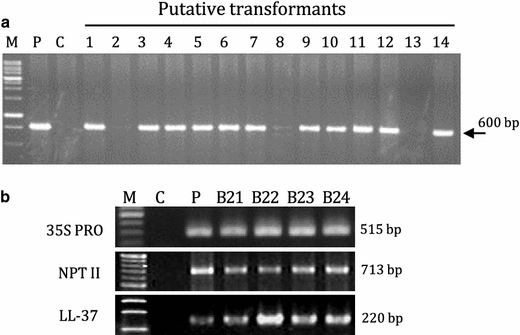
PCR amplification of the foreign genes in the transgenic Chinese cabbage lines. a PCR analysis of 14 putative LL-37 Chinese cabbage lines (T0) using the 35SF (5′-ATGGAGTCAAAGATTCAAATAGAG-3′) and LL-37R (5′-CGAGAGCTCCTAGGACTCTGTCCTGGG-3′) primers. Lanes: M 1 kb ladder, P positive control (pBI LL-37), C non-transformed plant, 1–14 putative transformants. b Four T3 (B21, 22, 23, 24) of single transgenic homozygous lines from T2 (B11, 12, 13, 14) were reconfirmed by PCR after genetic segregation events by kanamycin resistance. Amplification products of the 35S promoter, NptII, and LL-37 were separated using a 1.5% agarose gel. Lanes: M DNA ladder, C non-transformed plant, P pBILL-37, B21–B24 independent T3 transgenic homozygous lines
Expression of LL-37 in homozygous lines
In order to confirm LL-37 expression in the transformants, we performed quantitative RT-PCR using total RNA from 4 homozygous lines. The results of RT-PCR indicated that LL-37 RNA was expressed in the homozygous lines, and the expression levels were similar across all the transformants (Fig. 3). Western blot analysis also confirmed that the four homozygous lines expressed the 4-kDa peptide at varying levels, whereas the control plants did not show the LL-37-specific band (Fig. 4). Therefore, we concluded that the antimicrobial LL-37 gene was stably integrated into the genome of the transformants and was transcribed into mRNA that yielded the LL-37 peptide.
Fig. 3.
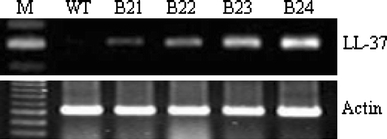
Analysis of the LL-37 gene expression in the transgenic homozygous lines by using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Total RNA was isolated from each plant, and 0.5 μg of this RNA was amplified with LL-37-specific primers. The Chinese cabbage actin gene was amplified as a loading control. The amplification products of the LL-37 gene were separated using a 1.5% agarose gel. Lanes: M DNA ladder, WT wild-type plant, B21–B24 independent transgenic homozygous lines
Fig. 4.

Western blot analysis of transgenic homozygous lines. Lanes: WT wild-type plant, B21–B24, transgenic homozygous lines containing the LL-37 gene, arrow indicates 4 kDa protein
Increased resistance of the transgenic plants to soft rot
The resistance to several rot pathogens was evaluated for the four homozygous lines harboring the human LL-37 gene by comparing the severity of the disease to that seen with the nontransgenic plants. Transgenic and control plants were inoculated with conidia, and the sizes of the disease lesions were determined. In order to test the resistance of the transgenic plants, we first cultivated the cabbage soft rot pathogen P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum in LB medium for 1–2 days. We tested the resistance of the plants to three different concentrations of the bacterial pathogen: 104, 106, and 108 CFU/mL. We challenged the leaf body and leaf vein with 104 and 106 CFU/mL of the bacterial culture, respectively; subsequently, the pathogenesis at the leaf was examined after 24, 48, and 72 h of inoculation. The control cabbage plants were susceptible to the bacterial pathogen and their leaves became softer with visible lesions 12 h after inoculation. After 48 h, the symptom spread all over the leaves, and the plants died owing to softening 72 h after inoculation of the pathogen. On the other hand, the softening symptom was not observed in three of the four transgenic lines, B21, B22, and B24, by 72 h after bacterial inoculation (Fig. 5). When 108 CFU/mL of the bacterial culture was inoculated, the leaves of the control plants showed the softening symptom 12 h after inoculation; the condition worsened and the leaves became amorphous after 24 h of inoculation. The transgenic lines only showed mild softening of the leaves around the area of inoculation (Fig. 6). Therefore, it could be concluded that transgenic plants showed significantly increased resistance to the bacterial pathogen P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum, which causes soft rot.
Fig. 5.
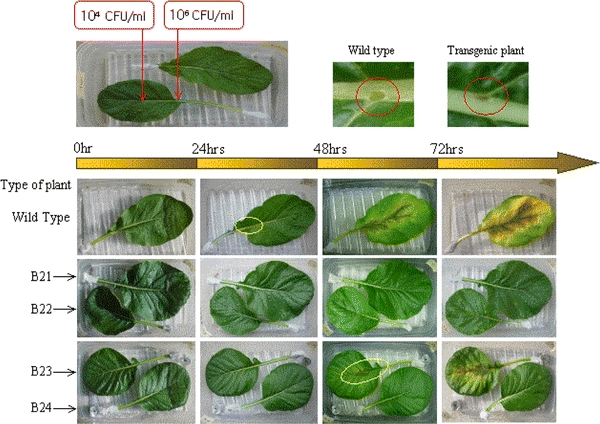
Temporal development of soft rot in Chinese cabbage (“Osome”) plants when the leaves were inoculated with Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum. B21–B24 Transgenic homozygous lines
Fig. 6.
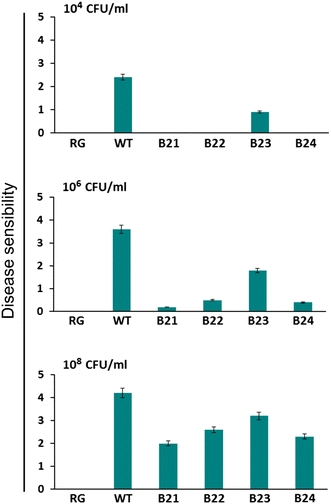
Disease development in transgenic homozygous lines containing the LL-37 gene, which were inoculated with 104, 106, or 108 CFU/mL of P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum. Disease manifestations were scored 3 days after inoculation. RG water, WT wild-type plant, B21–B24 LL-37 transgenic homozygous lines. Disease lesions: 0, no lesion; 1, lesion size 0.1–0.5 cm; 2, 0.5–1.5 cm; 3, 1.5–3.5 cm; 4, 3.5–5.5 cm; 5, 5.5–8.5 cm; and 6, over 8.5 cm or plant dead
Increased resistance of the transgenic plants to fungal pathogens
The leaves of the transgenic plants were challenged with several fungal pathogens such as F. oxysporum, C. higginsianum, and R. solani in order to test the resistance of the transgenic plants to fungal pathogens. Three of the four transgenic homozygous lines, B21, B22, and B23, showed higher resistance to F. oxysporum than the control plants (Fig. 7). In particular, B21 showed remarkably high resistance to F. oxysporum. After being challenged with C. higginsianum and R. solani, the control plants showed typical symptoms and died after 6 days of inoculation, while the transgenic plants were resistant, as shown in Fig. 7. Therefore, we can conclude that the LL-37 peptide expressed in the transgenic plants acts as an effective antimicrobial peptide.
Fig. 7.
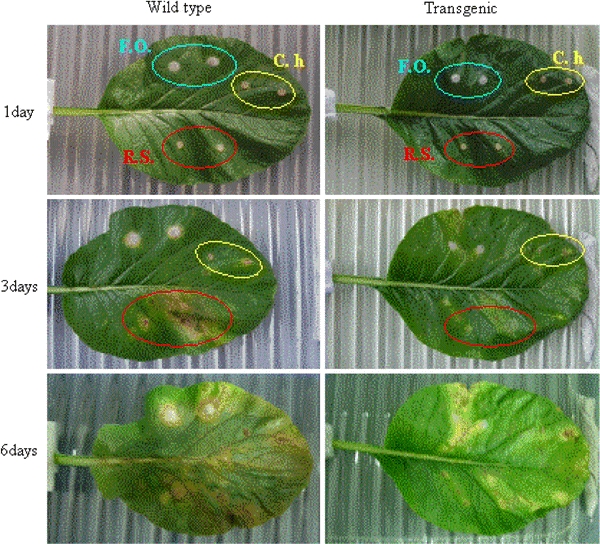
Enhanced disease resistance of transgenic homozygous lines to several fungal pathogens. F.O., Fusarium oxysporum; C.h., Colletotrichum higginsianum; R.S., Rhizoctonia solani. Disease manifestations assessed until 6 days after inoculation
Bacterial inhibition assays in transgenic leaflets
We collected TF and EF from the leaflets of three transgenic homozygous lines and a non-transformed line in order to study their effects on the activity of LL-37. The inhibition of the bacterial (P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum) growth by TF and EF was evaluated using the spectrophotometric method. As expected, bacteria grew normally when they were incubated in LB medium only and in TF or EF obtained from the non-transformed line, while the growth was completely inhibited when EF obtained from the three transgenic lines was added to the LB medium (Fig. 8). Bacteria also grew well in the TF obtained from the three transgenic lines, although their growth was lower than that in LB medium alone.
Fig. 8.
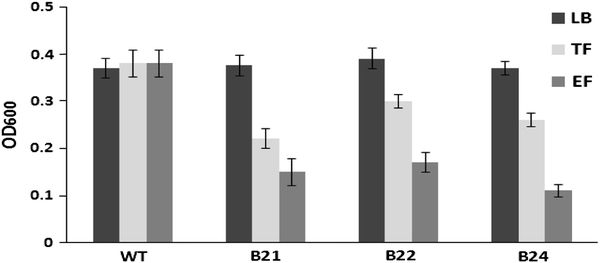
Bacterial inhibition assays of total fluid (TF) and extracellular fluid (EF) obtained from the leaflets of transgenic homozygous lines; LB Luria–Bertani medium
Discussion
In response to a microbial attack, plants activate a complex series of responses that lead to the local and systemic induction of a broad spectrum of antimicrobial defenses (Kim and Martin 2004; Kunkel 2002). When induced defense responses are rapidly and coordinately triggered during a given plant–pathogen interaction, plants become broadly resistant to diseases. These defense responses include the strengthening of mechanical barriers, oxidative burst, and production of antimicrobial compounds (Hammond-Kosack and Parker 2003; Park 2005). Some research has been performed to bolster plant defenses against bacteria and fungi by genetically engineering plants to express antimicrobial peptides (Lee et al. 2008; Prasad et al. 2008).
In this study, we have chosen a variant of the antimicrobial peptide LL-37 as an interesting candidate for transgenic plant expression; this variant is designed to target the peptide into extracellular spaces. Extracellular targeting was originally intended to prevent possible deleterious effects of the peptide in plant cells. Moreover, secretion into extracellular spaces allows the plant-produced peptide to come into direct contact with pathogens growing and multiplying extracellularly before attacking the cells (Ponti et al. 2003). We developed homozygous Chinese cabbage lines stably expressing LL-37, which did not cause adverse effects on the plant phenotypes. These transgenic homozygous lines were tested with four important pathogens of this crop and found to inhibit the growth of the bacterial pathogen causing Chinese cabbage rot and also that of three fungal pathogens.
The results of our pathogenicity assays suggest that the expression of LL-37 provides a moderate level of resistance against a bacterial pathogen (P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum) at the inoculum concentration of 104 CFU/mL. However, the extent of disease suppression provided by LL-37 expression was reduced as the inoculum concentrations were increased to 106 and 108 CFU/mL. Moreover, we observed reduction in the survival of P. carotovorum subsp. carotovorum cells incubated with EF from LL-37-expressing Chinese cabbage cell lines. However, bacteria grew normally when they were incubated in LB medium only and in TF or EF obtained from a non-transformed cell line. Therefore, leaves appeared to express LL-37 at sufficient levels in the extracellular spaces to retard bacterial multiplication and hence decrease disease severity. The functionality of this transgene and the presence of antimicrobial activity in the EF indicates that the LL-37 peptide was properly targeted to the extracellular space even with a foreign plant signal peptide. Furthermore, the mammalian peptide was not subjected to a processing step in the foreign plant cell environment that rendered it inactive.
Until now, studies involving the enhancement of resistance to various bacterial, fungal, and oomycete pathogens by the expression of antimicrobial peptides have been reported for rice, tobacco, poinsettia, banana, and more host species (Chakrabarti et al. 2003; Liang et al. 2002; Smith et al. 1998). However, progress on identifying the defense mechanisms in Chinese cabbage (B. rapa), an important vegetable crop in Asia, has been very slow. Previously, we reported an enhancement in the resistance to bacterial soft rot by the expression of the bromelain gene in Chinese cabbage (Jung et al. 2008). Here, we demonstrate that expression of the human LL-37 peptide has antimicrobial activity toward both bacterial and fungal pathogens of Chinese cabbage. Since pathogens have the ability to overcome gene-for-gene host defense mechanisms in the field by undergoing mutations in the cognate avirulence genes, any transgenic model based on such resistance-conferring genes may easily be evaded by pathogens. On the other hand, this problem is less likely to occur in transgenic plants overexpressing genes with more general antimicrobial activity. Therefore, the expression of the human LL-37 peptide is expected to confer durable resistance (i.e., field resistance) to a wide variety of pathogens infecting Chinese cabbage plants.
In order to obtain a high level of resistance as observed in the case of R gene-mediated resistance, the overexpression of multiple antifungal proteins with different functions may be necessary. In a R. solani infection assay, tobacco plants coexpressing the barley transgenes (a class II chitinase, a class II β-1,3-glucanase, and a type I ribosome-inactivating protein) were reported to elicit significantly enhanced protection against fungal attack as compared to that of the corresponding isogenic lines expressing a single barley transgene at a similar level (Brogue et al. 1991). Thus, other antimicrobial genes such as the bromelain gene (Jung et al. 2008) could be stacked with the human LL-37 gene by crossing different transgenic lines and this may be able to strongly and durably inhibit the growth of pathogens.
Acknowledgments
We thank to Dr. Philip Becraft for critical reviews and comments. This work was supported by a grant from the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (No. PJ008085), Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
References
- Alan AR, Blowers A, Earle ED. Expression of a magainin-type antimicrobial peptide gene (MSI-99) in tomato enhances resistance to bacterial speck disease. Plant Cell Rep. 2004;22:388–396. doi: 10.1007/s00299-003-0702-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieri S, Potrykus I, Fütterer J. Effects of combined expression of antifungal barley seed proteins in transgenic wheat on powdery mildew infection. Mol Breed. 2003;11:37–48. doi: 10.1023/A:1022145915983. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Boman HG. Antibacterial peptides: basic facts and emerging concepts. J Intern Med. 2003;254:197–215. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2796.2003.01228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brogue K, Chet I, Holliday M, Cressman R, Biddle P, Knowlton S, Mauvais CJ, Broglie R. Transgenic plants with enhanced resistance to the fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia solani. Science. 1991;254:1194–1197. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5035.1194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti A, Ganapathi TR, Mukherjee PK, Bapat VA. MSI-99, a magainin analogue, imparts enhanced disease resistance in transgenic tobacco and banana. Planta. 2003;216:587–596. doi: 10.1007/s00425-002-0918-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C, Chen Z. Potentiation of developmentally regulated plant defense response by AtWRKY18, a pathogen-induced Arabidopsis transcription factor. Plant Physiol. 2002;129:706–716. doi: 10.1104/pp.001057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Smet K, Contreras R. Human antimicrobial peptides: defensins, cathelicidins and histatins. Biotechnol Lett. 2005;27:1337–1347. doi: 10.1007/s10529-005-0936-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelvin SB. The introduction and expression of transgenes in plants. Curr Opin Biotech. 1998;9:227–232. doi: 10.1016/S0958-1669(98)80120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudmundsson GH, Agerberth B, Odeberg J, Bergman T, Olsson B, Salcedo R. The human gene FALL39 and processing of the cathelin precursor to the antibacterial peptide LL-37 in granulocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1996;238:325–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0325z.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond-Kosack KE, Parker JE. Deciphering plant-pathogen communication: fresh perspectives for molecular resistance breeding. Curr Opin Biotech. 2003;14:177–193. doi: 10.1016/S0958-1669(03)00035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung YJ, Choi CS, Park JH, Kang HW, Choi JE, Nou IS, Lee SY, Kang KK. Overexpression of the pineapple fruit bromelain gene (BAA) in transgenic Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa) results in enhanced resistance to bacterial soft rot. Electron J Biotechnol. 2008;11:1–8. doi: 10.2225/vol11-issue1-fulltext-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kim YJ, Martin GB. Molecular mechanisms involved in bacterial speck disease resistance of tomato. Plant Pathol J. 2004;20:7–12. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.2004.20.1.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel BN. Brooks cross talk between signaling pathways in pathogen defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2002;5:325–331. doi: 10.1016/S1369-5266(02)00275-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee SC, Hwang IS, Choi HW, Hwang BK. Involvement of the pepper antimicrobial protein CaAMP1 gene in broad spectrum disease resistance. Plant Physiol. 2008;143:1004–1020. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.123836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang H, Catranis CM, Maynard CE, Powell WA. Enhanced resistance to the poplar fungal pathogen, Septoria musiva, in hybrid poplar clones transformed with genes encoding antimicrobial peptides. Biotechnol Lett. 2002;24:383–389. doi: 10.1023/A:1014552503140. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Makandar R, Essig JS, Schapaugh MA, Trick HN, Shah J. Genetically engineered resistance to Fusarium head blight in wheat by expression of Arabidopsis NPR1. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2006;19:123–129. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-19-0123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min BW, Cho YN, Song MJ, Noh TK, Kim BK, Chae WK, Park YS, Choi YD, Harn CH. Successful genetic transformation of Chinese cabbage using phosphomannose isomerase as a selection marker. Plant Cell Rep. 2007;26:337–344. doi: 10.1007/s00299-006-0247-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park JM. The hypersensitive response: a cell death during disease resistance. Plant Pathol J. 2005;21:99–101. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.2005.21.2.099. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ponti D, Mangoni ML, Mignogna G, Simmaco M, Barra D. An amphibian antimicrobial peptide variant expressed in Nicotiana tabacum confers resistance to phytopathogens. Biochem J. 2003;370:121–127. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad BD, Jha S, Chattoo BB. Transgenic indica rice expressing Mirabilis jalapa antimicrobial protein (Mj-AMP2) shows enhanced resistance to the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Plant Sci. 2008;175:364–371. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2008.05.015. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy KV, Yedery RD, Aranha C. Antimicrobial peptides: premises and promises. Int J Antimicrob Ag. 2004;24:536–547. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2004.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniaatis T. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. 2. Cold Spring Harbor, New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Simmaco M, Mignogna G, Barra D. Antimicrobial peptides from amphibian skin: what do they tell us? Biopolymers. 1998;47:435–450. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0282(1998)47:6<435::AID-BIP3>3.0.CO;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith FD, Gadoury DM, Vaneck JM, Blowers A, Sanford JC, Van der Meij J, Eisenreich R. Enhanced resistance to powdery mildew in transgenic poinsettia conferred by antimicrobial peptides. Phytopathology. 1998;88:S83. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn KH, Lee SC, Jung HW, Hong JK, Hwang BK. Expression and functional roles of the pepper pathogen-induced transcription factor RAV1 in bacterial disease resistance, and drought and salt stress tolerance. Plant Mol Biol. 2006;61:897–915. doi: 10.1007/s11103-006-0057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen OE, Follin P, Johnsen AH, Calafat J, Tjabringa GS, Hiemstra PS, Borregaard N. Human cathelicidin, hCAP-18, is processed to the antimicrobial peptide LL-37 by extracellular cleavage with proteinase 3. Blood. 2001;97:3951–3959. doi: 10.1182/blood.V97.12.3951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis SM, Anderson NN, Forsyth WR, Espiritu C, Conway BD, Greenberg EP, McCray PB, Lehrer RI, Welsh MJ, Tack BF. Bactericidal activity of mammalian cathelicidin-derived peptides. Infect Immun. 2000;68:2748–2755. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.5.2748-2755.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki K, Schauber J, Coda A, Lin H, Dorschner RA, Schechter NM, Bonnart C, Descargues P, Hovnanian A, Gallo RL. Kallikrein-mediated proteolysis regulates the antimicrobial effects of cathelicidins in skin. Fed Am Soc Exp Biol J. 2006;20:2068–2080. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-6075com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X, Dai Y, Xiong Y, DeFraia C, Li J, Dong X, Mou Z. Overexpression of ArabidopsisMAP kinase kinase 7 leads to activation of plant basal and systemic acquired resistance. Plant J. 2007;52:1066–1079. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


