Fig. 1. Ribbon diagram of AphB.
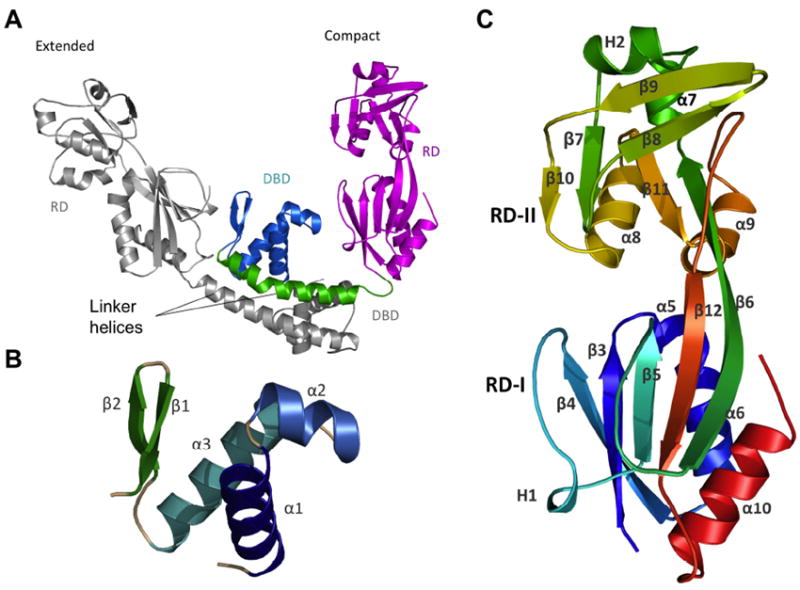
(A) The asymmetric unit of the full-length AphB structure contains one extended subunit (grey) and one compact subunit (color) that dimerize through their linker helices to form a coiled-coil. In the compact subunit, the DNA-binding domain (DBD, cyan) and linker helix (green) are folded in toward the regulatory domain (RD, magenta), whereas in the extended subunit, the DNA-binding domain and linker helix point away from the RD. (B) The DNA binding domain (residues 1-58) of AphB consists of a winged helix-turn-helix motif. (C) The regulatory domain of AphB contains two subdomains: RD-1 (residues 90-159 and residues 262-291) and RD-II (residues 160-261) colored from N-terminal residue (S90, blue) to the C-terminus (red). All figures were created using MacPyMOL (DeLano, 2002).
