Fig. 2. Ribbon diagram of the AphB tetramer.
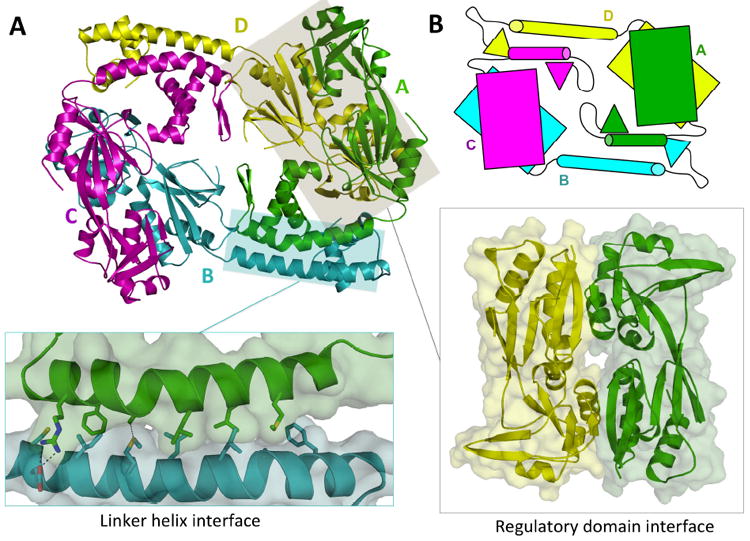
(A) The AphB tetramer is composed of four subunits, two in the extended (yellow, cyan) conformation and two in the compact (magenta, green) conformation. The N-terminal dimerization interface (left inset), along the linker helices of subunit A and B, is composed of polar, charged and hydrophobic residues. The head-to-tail interaction of the regulatory domain of subunit A with the regulatory domain of subunit D forms the second dimerization interface (right inset). (B) Schematic showing the overall fold of AphB, which is formed by four subunits, each composed of a regulatory domain (rectangles) connected to a DNA-binding domain (triangles) via a linker helix (cylinders).
