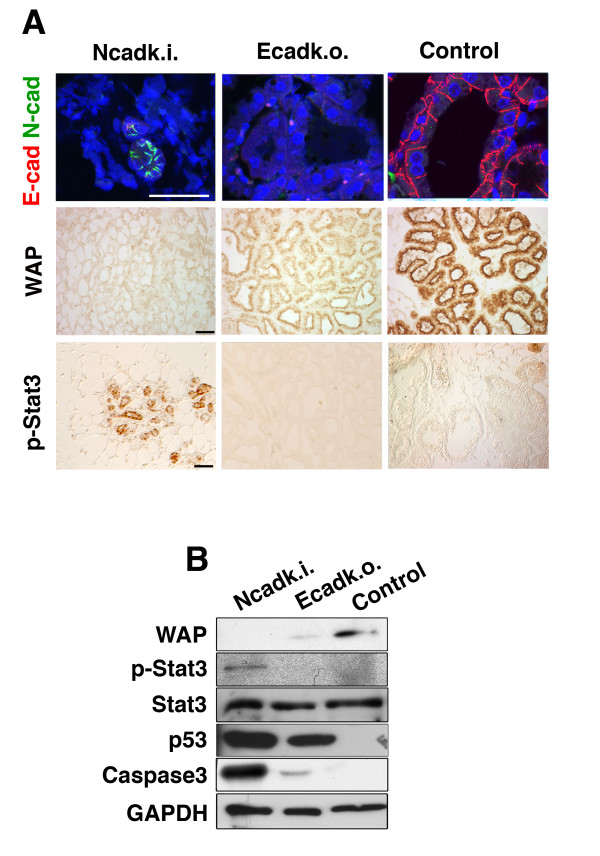
Figure 2.
Ncadk.i. mammary glands exhibit signs of precocious involution. (A) Immunofluorescence of paraffin sections revealed a mislocalization of N-cad in collapsed alveoli of Ncadk.i. mammary glands. No E-cad could be detected in Ecadk.o. alveoli, which looked morphologically normal. In control samples, E-cad but not N-cad, could be found at the basolateral site of alveolar epithelial cells. DAPI was used to visualize nuclei of the cells. The alveoli of Ecadk.o. females show immunoreactivity for WAP while WAP is completely absent in Ncadk.i. alveoli. P-Stat3, a key player in the involution process, is highly upregulated in Ncadk.i., whereas Ecadk.o. and control did not show any signal for p-Stat3. Scale bar: 100 μm. (B) Western Blot analysis of mammary glands on the second day of the second lactation cycle. WAP is highly decreased in Ecadk.o. and completely absent in Ncadk.i. mammary glands compared to control. P-Stat3 is induced in Ncadk.i., indicating involution. P53, an inducer of apoptosis, is highly upregulated in Ncadk.i. and Ecadk.o.; however, cleaved caspase3 was predominantly detected in Ncadk.i. mammary glands. GAPDH was used to ensure the loading of equal amounts of proteins. Control, WAP::Cre;Ecadfl/+ ; DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; E-cad, E-cadherin; Ecadk.o., WAP::Cre;Ecadfl/fl; GAPDH, Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; N-cad, N-cadherin; Ncadk.i., WAP::Cre;EcadNcad/fl;p53, protein 53; P-Stat3, Phospho Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; WAP, Whey acidic protein.