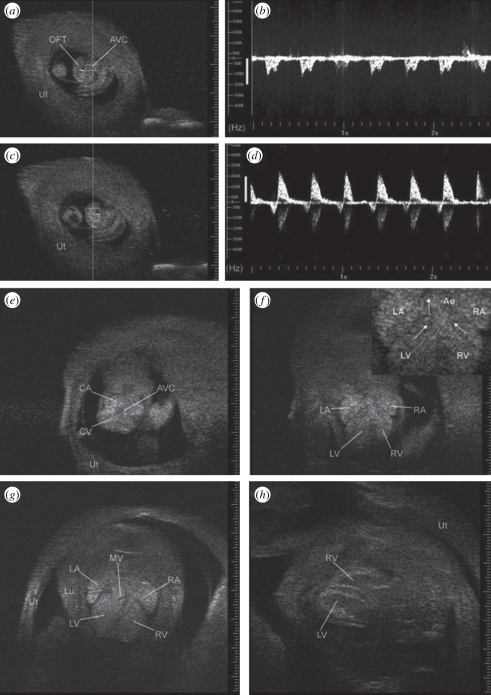
Figure 4.
Images of the embryonic heart as it develops from a U-shaped tube at E9.5 to a four-chambered structure at E16.5 when viewed through the exteriorized uterus (Ut) using 55 MHz. (a) U-shaped embryonic heart at E9.5. Doppler sample volume (rectangle) within atrioventricular canal (AVC) generated ventricular inflow Doppler waveform in (b). (c) Doppler sample volume in the outflow tract (OFT) generated the Doppler waveform in (d). (e) Transverse view at E10.5 showing common atrium (CA), common ventricle (CV), and common atrioventricular canal (AVC). (f) Transverse view at E12.5 showing left and right atrium (LA, RA) and left and right ventricle (LV, RV) with enlargement in inset with arrows highlighting streamlines towards the aorta (Ao). (g) Transverse view at E13.5 with mitral valve leaflets (MV) and complete septum visible (Lu, lung). (h) Long-axis view of ventricles at E16.5. Echogenicity of embryonic blood tends to reduce blood–tissue contrast but this effect attenuates near term. Adapted from [22].