Abstract
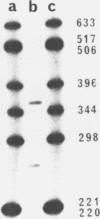
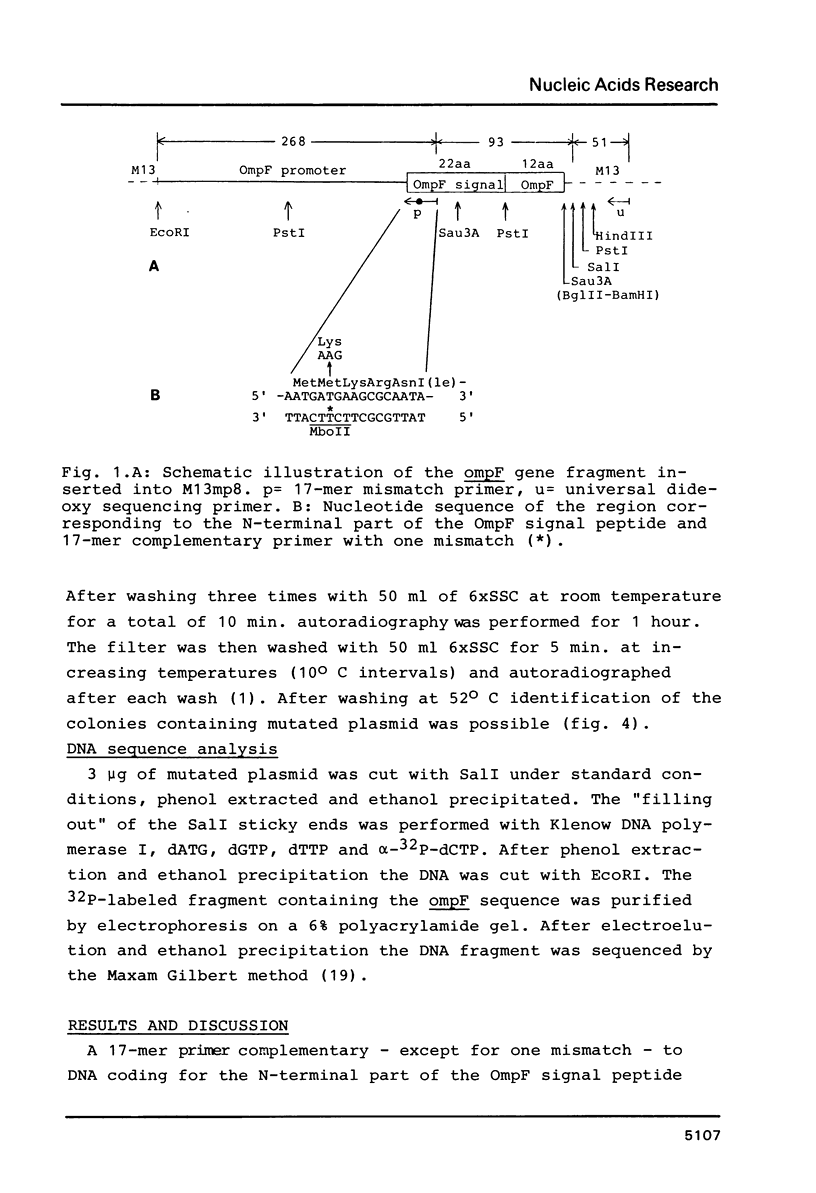
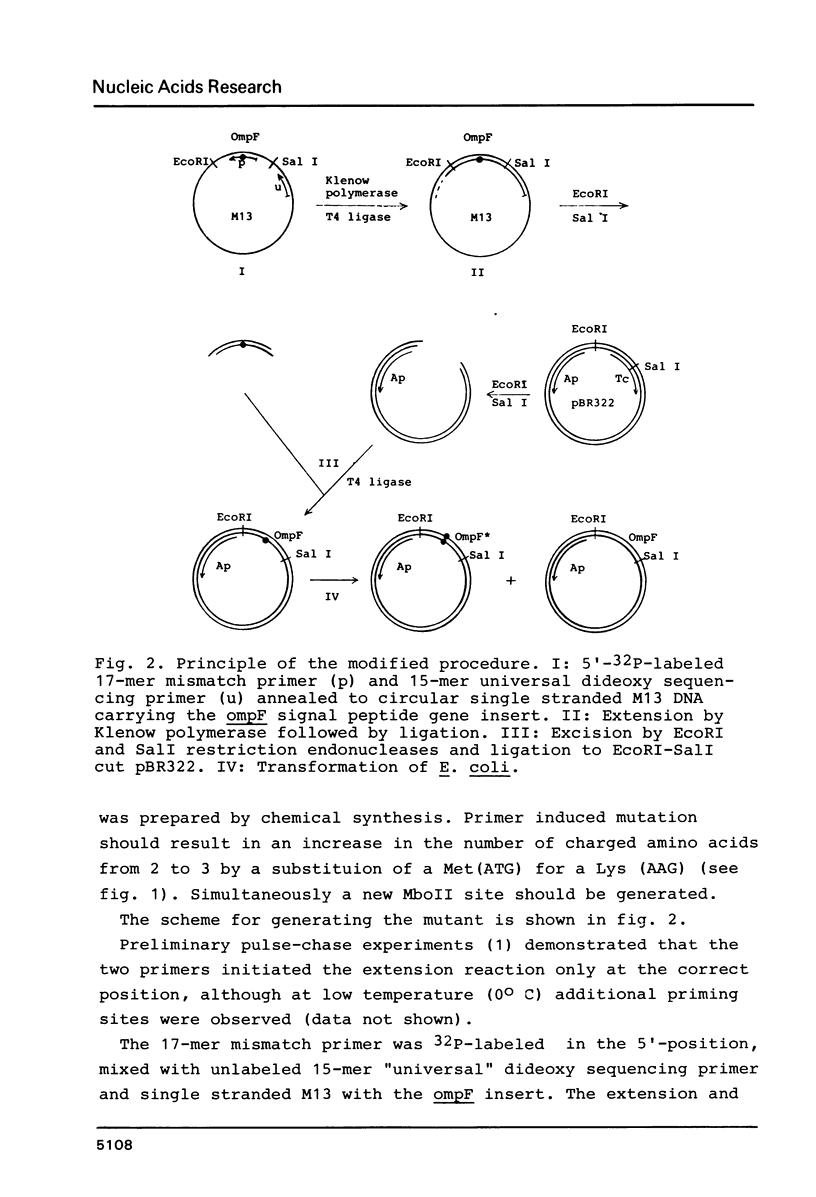
A rapid and efficient procedure for site specific mutagenesis is described. A double primed synthesis with a 17-mer mismatch primer and a "universal" 15-mer M13 sequencing primer was used to introduce a T to A transversion into an ompF signal peptide gene cloned in the M13mp8 vector. The two primers were annealed to the circular single stranded M13 template. After a short extension and ligation reaction, a double stranded restriction fragment containing the mismatch (ompF*/EcoR1-SalI) was cut out of the partly single stranded circular DNA and inserted into pBR322. 42% of the E.coli transformants harboured plasmid with the desired mutation, which could be detected by the appearance of a new restriction site (MboII) and by dot blot hybridization of plasmid DNA with the 32P-labeled 17-mer.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Chou J., Cohen S. N. In vitro gene fusions that join an enzymatically active beta-galactosidase segment to amino-terminal fragments of exogenous proteins: Escherichia coli plasmid vectors for the detection and cloning of translational initiation signals. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):971–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.971-980.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth M. L., Gait M. J., Goelet P., Hong G. F., Singh M., Titmas R. C. Rapid synthesis of oligodeoxyribonucleotides VI. Efficient, mechanised synthesis of heptadecadeoxyribonucleotides by an improved solid phase phosphotriester route. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1691–1706. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz H. J., Belagaje R., Brown E. L., Fritz R. H., Jones R. A., Lees R. G., Khorana H. G. High-pressure liquid chromatography in polynucleotide synthesis. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1257–1267. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Silhavy T. J. The ompB locus and the regulation of the major outer membrane porin proteins of Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 15;146(1):23–43. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90364-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidecker G., Messing J., Gronenborn B. A versatile primer for DNA sequencing in the M13mp2 cloning system. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):69–73. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inokuchi K., Mutoh N., Matsuyama S., Mizushima S. Primary structure of the ompF gene that codes for a major outer membrane protein of Escherichia coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6957–6968. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Soberon X., Franceschini T., Nakamura K., Itakura K., Inouye M. Role of positive charge on the amino-terminal region of the signal peptide in protein secretion across the membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3438–3441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Ike Y., Ikuta S., Itakura K. Solid phase synthesis of polynucleotides. VI. Further studies on polystyrene copolymers for the solid support. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1755–1769. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Schughart K., Fritz H. J. Directed mutagenesis of DNA cloned in filamentous phage: influence of hemimethylated GATC sites on marker recovery from restriction fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6475–6485. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M. The effect of site specific methylation on restriction endonuclease cleavage (update). Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):r169–r173. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.235-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Keem K., Monahan J. J. Factors affecting the transformation of Escherichia coli strain chi1776 by pBR322 plasmid DNA. Gene. 1978 Jul;3(4):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Urieli S., Pollack Y., Gruenbaum Y., Glaser G. Studies on the biological role of dna methylation; IV. Mode of methylation of DNA in E. coli cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 25;8(8):1783–1792. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.8.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson M. J., Hirose T., Miyake T., Kawashima E. H., Itakura K. The use of synthetic oligonucleotides as hybridization probes. II. Hybridization of oligonucleotides of mixed sequence to rabbit beta-globin DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):879–894. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Schold M., Johnson M. J., Dembek P., Itakura K. Oligonucleotide directed mutagenesis of the human beta-globin gene: a general method for producing specific point mutations in cloned DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3647–3656. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter G., Fersht A. R., Wilkinson A. J., Zoller M., Smith M. Redesigning enzyme structure by site-directed mutagenesis: tyrosyl tRNA synthetase and ATP binding. Nature. 1982 Oct 21;299(5885):756–758. doi: 10.1038/299756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarucki-Schulz T., Tsai S. Y., Itakura K., Soberon X., Wallace R. B., Tsai M. J., Woo S. L., O'Malley B. W. Point mutagenesis of the ovalbumin gene promoter sequence and its effect on in vitro transcription. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11070–11077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]