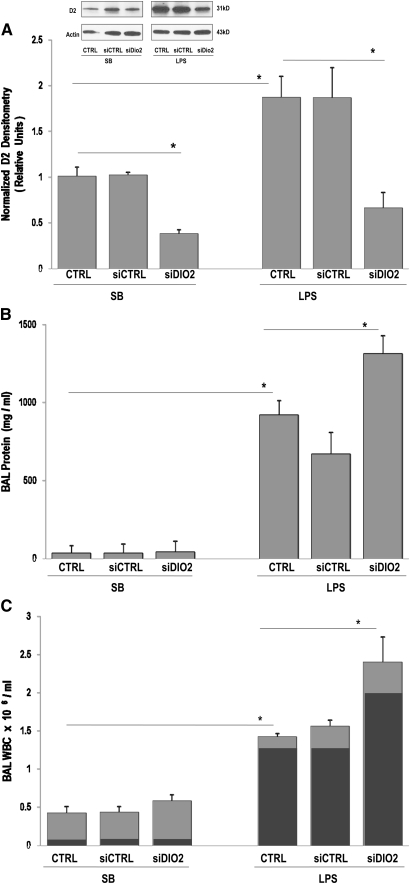
Figure 4.
LPS-induced lung injury is augmented by siDIO2. (A) In vivo silencing effect of custom-designed siDIO2 in lung homogenates was confirmed by Western blotting (inset), quantified by densitometry, and expressed in bar graphs as normalized D2 densitometry in relative units. A significant reduction of D2 expression was observed in siDIO2-pretreated SB mice compared with vehicle control (CRTL) or scrambled siRNA (siCTRL) mice. D2 level augmented by LPS was markedly reduced by siDIO2 compared with LPS vehicle control (CRTL) or scrambled siRNA (siCTRL). (B) BAL protein levels in SB and LPS mice. Significant increase of BAL proteins was observed in siDIO2-pretreated SB or LPS mice compared with CRTL or siCTRL mice. (C) BAL leukocytes (WBC) were expressed as 106/ml in SB and LPS mice. A significant increase of BAL leukocytes (light gray bars) represented primarily by increased neutrophil influx (dark gray bars) was observed in siDIO2-pretreated SB or LPS mice compared with CRTL or siCTRL mice. LPS (1 mg/kg) was intratracheally administrated for 18 hours for the LPS model. Minimal inflammatory cells were observed in SB treated with vehicle control (CTRL) or siCTRL, whereas inflammation and protein leak were increased in LPS mice (CTRL or siCTRL). siDIO2 (10 mg/kg) or siCTRL was delivered intratracheally 72 hours before the experiments. Results are from at least five independent experiments; *P < 0.05.