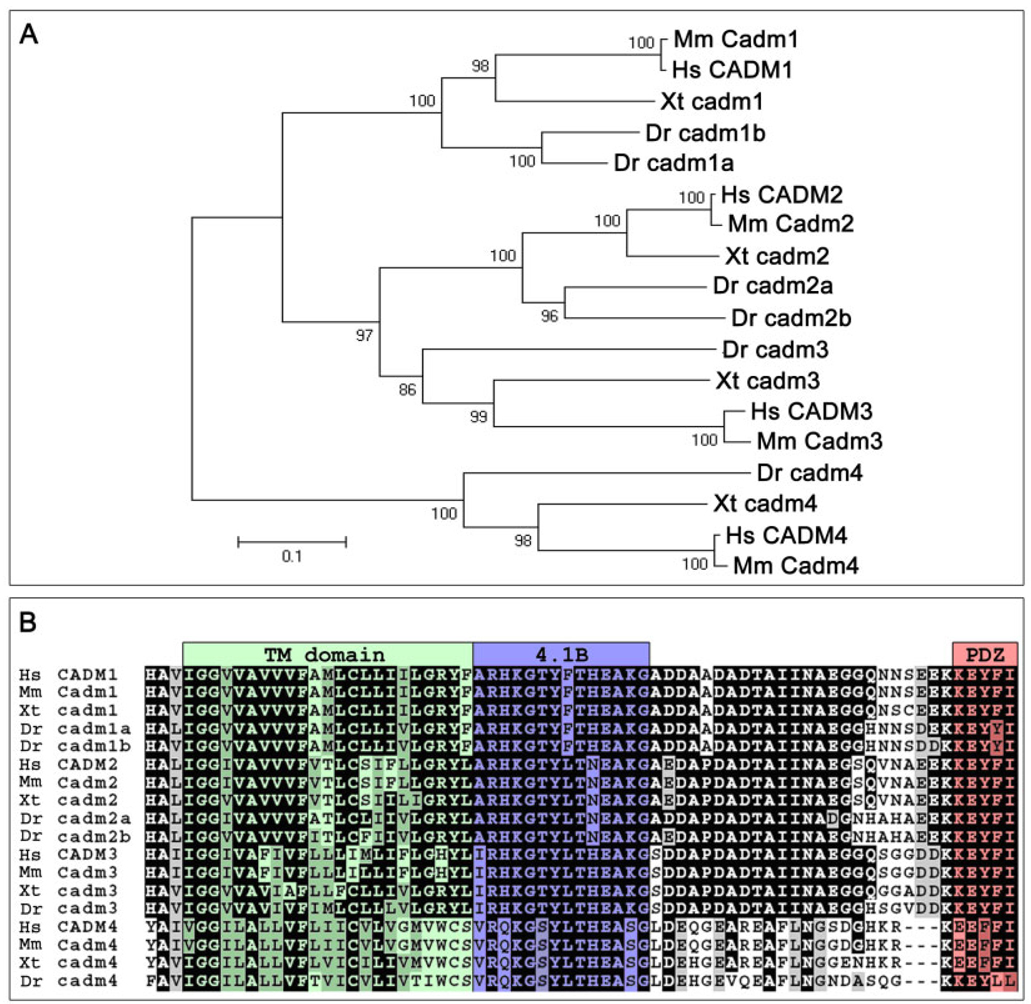
Fig. 2.
Phylogeny of the Cadm proteins. A: Relationships between the Cadm protein sequences of various vertebrates (Hs, Homo sapiens; Mm, Mus musculus; Xt, Xenopus tropicalis; Dr, Danio rerio) are shown in a phylogenetic tree. Amino acid sequences were aligned by Clustal-X. Sequences were trimmed to include unambiguously aligned regions, and phylogenic analysis used the Poisson-corrected neighbor-joining method. The branch lengths (numbers) are the percentage of bootstrap values for 1,000 replicas. Scale bar = 0.1 substitutions per site. B: Alignment of the transmembrane domain and cytoplasmic tail of the Cadm proteins highlights the high level of conservation of the structural domains among vertebrates. Conserved positions with an identical amino acid (black) and conserved subtitutions (gray) have been shadowed; the color shading of domains is as in Figure 1A.