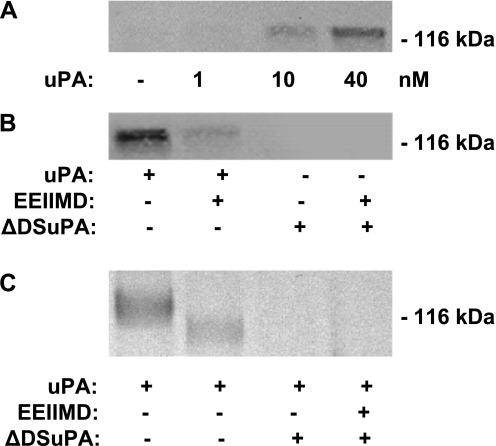
Figure 5.
Interaction of uPA and NMDA-R1 in pulmonary arteries. (A) uPA binds to NMDA-R from the pulmonary artery. Homogenates of pulmonary arterial rings isolated from uPA−/− mice were preincubated with the indicated concentrations of uPA at 4°C, and precipitated with an antibody against uPA, followed by immunoblotting with an antibody against the NR1 subunit of NMDA-R1. The results of an experiment representative of three independent analyses are shown. (B) The docking sites in uPA mediate its interactions with NMDA-R. As in A, homogenates of pulmonary arteries rings isolated from uPA−/− mice were preincubated with WT uPA (40 nM) (uPA), WT uPA with PAI-1 derived peptide EEIIMD (EEIIMD, 1 μM), or the uPA variant that lacks a functional docking site (ΔDSuPA) at 4°C, precipitated with an antibody against uPA, followed by immunoblotting with an antibody against the NR1 subunit of NMDA-R1. The results of an experiment representative of three independent analyses are shown. (C) uPA cleaves the NR1 subunit of NMDA-R1. Pulmonary arterial rings isolated from uPA−/− mice were incubated in buffer alone or buffer containing 20 nM WT uPA (uPA), WT uPA with PAI-1–derived peptide EEIIMD (1 μM), or the uPA variant that lacks a functional docking site (ΔDSuPA) for 120 minutes at 37°C. Tissue homogenates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting, using an antibody against the NR1 subunit of NMDA-R1. The results of an experiment representative of three independent analyses are shown.