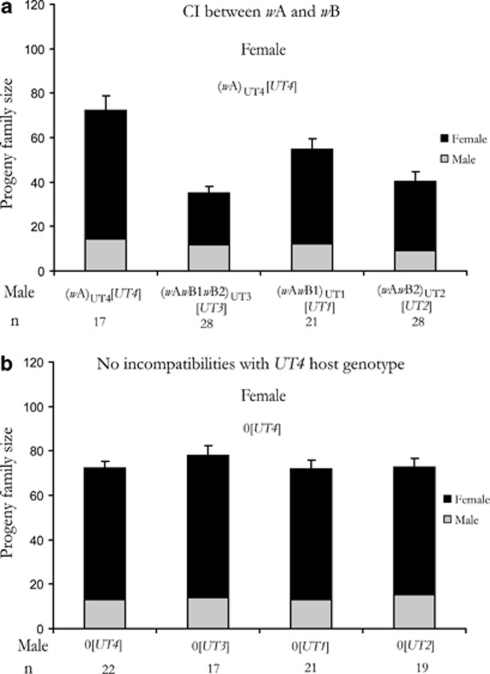
Figure 4.
All the three Wolbachia in N. longicornis represent distinct incompatibility types. (a) The A and the two B supergroup infections all represent distinct incompatibility types. All the three multiply infected males produce CI against the single wA-infected females. The first column is the intra-strain control of the single A-infected strain (wA)UT4[UT4]. The second, third and fourth column represents the progeny family size when the females of this strain were crossed with males from (wAwB1wB2)UT3[UT3], (wAwB1)UT1[UT1] and (wAwB2)UT2[UT2], respectively. There is significant reduction in the progeny family size in each of these crosses (see text for details). (b) The reduction in progeny number is not caused by host nuclear incompatibilities, as the same strains when cured of their Wolbachia show no significant reduction in progeny size. (MWU: U=253, P=0.063, U=242.0, P=0.801 and U=227.0, P=0.651, respectively).