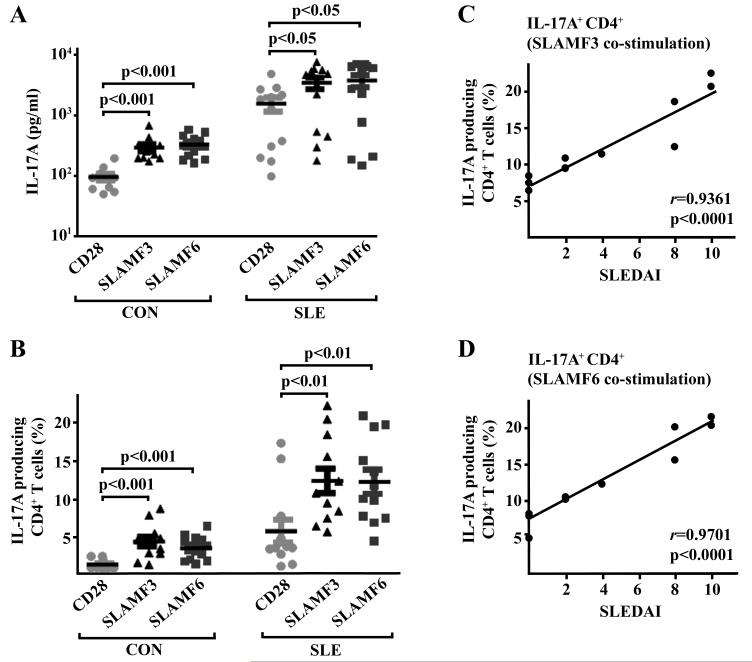
Figure 2. SLAM receptor co-stimulation enhances IL-17 production and reflects disease activity in SLE patients.
(A) Total T cells obtained from 11 healthy controls (CON) and 11 SLE patients were cultured under Th17 differentiation conditions along with anti-CD3 antibodies and co-stimulatory anti-CD28, anti-SLAMF3 or anti-SLAMF6 antibodies as indicated for a total period of 6 days. Subsequently, supernatants were subjected to IL-17 measurement (ELISA). (B) Total T cells were cultured as outlined under (A). Intracellular IL-17 staining was performed gating on CD4+ T cells. (C) Total T cells were isolated from SLE patients and cultured under Th17 conditions along with anti-CD3 and anti-SLAMF3 antibodies for 6 days. Percentages of IL-17-producing CD4+ T cells were correlated to the individual SLE disease activity scores (SLEDAI). (D) Percentages of IL-17-producing CD4+ T cells isolated from SLE patients (under anti-CD3/anti-SLAMF6 co-stimulation) were correlated to the individual SLEDAI scores.