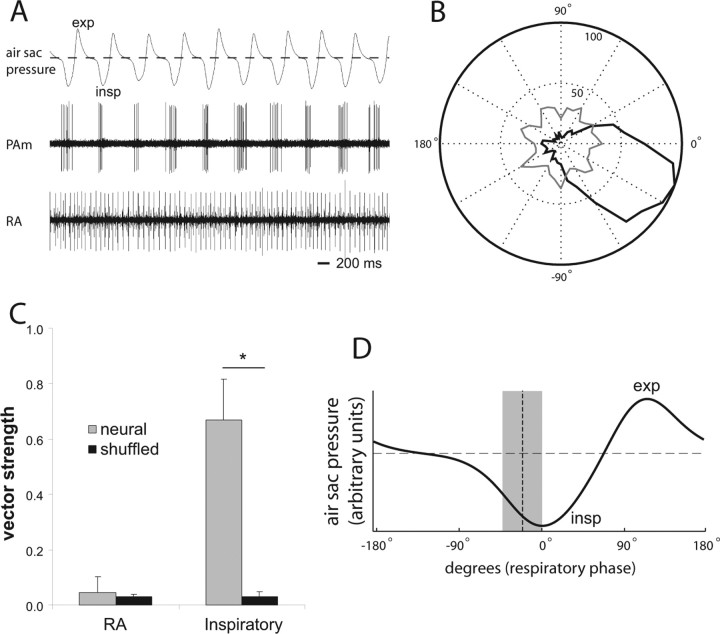
Figure 5.
Characterization of respiratory phase relationship in RA and PAm respiratory neurons. A, Simultaneous recordings of air sac pressure (top), single-unit activity in left PAm (middle), and unit activity in contralateral RA (bottom). Expiration (exp) is indicated as a positive deflection in the air sac pressure trace, whereas inspiration (insp) is indicated as negative deflections. The dotted line indicates ambient pressure. PAm units fire during or just preceding the negative deflection phase of respiration indicating that these units are phase locked to the inspiratory phase of respiration. B, A polar plot of spikes counted (radius) in an 80 s trace at different phases of respiration (angle). The count of PAm spikes is shown in black, and the RA spike count is shown in gray. In this figure, 0° is the approximate peak of the inspiratory phase. C, Mean vector strength for eight RA (left) and eight PAm inspiratory (right) neurons, compared with the mean of the vector strengths calculated by shuffling the spike times of each neuron's trace. The asterisk represents significance by two-tailed paired t tests. D, A canonical air sac pressure trace is shown for one respiratory cycle. The mean phase-relative timing of eight PAm inspiratory neurons is overlaid on the trace as a vertical dotted line. The surrounding gray box represents two SDs from this mean.