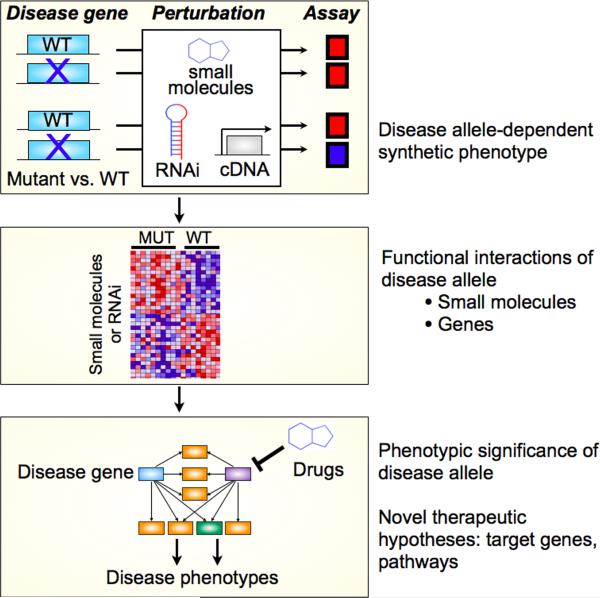
Fig. 3.
Perturbational screens on patient-derived cells can clarify the functional significance of disease alleles and lead to new therapeutic hypotheses. Using the logic of synthetic genetic interactions, patient cells can be screened for small molecules, RNAi, or cDNA that cause different phenotypes in cells that are mutant or wild-type at a disease gene. This identifies small molecules or genes that functionally interact with a disease gene, identifies pathways that may connect the disease allele to disease phenotypes, and provides clues for new therapeutic targets and hypotheses. Adapted from85.