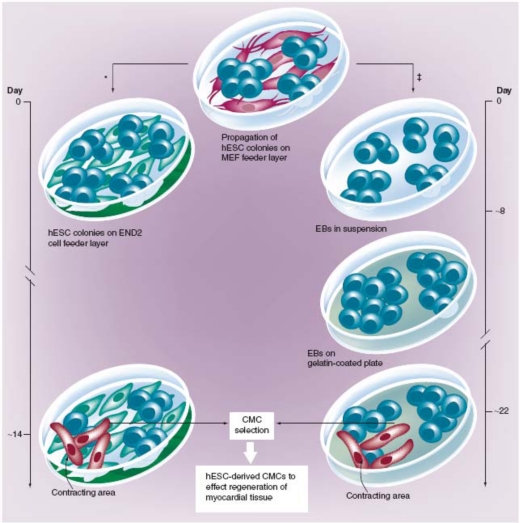
Fig. (1).
hESC propagation and in vitro differentiation into CMCs. hESC lines can be propagated continuously in the undifferentiated state when grown on top of an MEF feeder layer. With the Kehat protocol‡ [5], when hESCs are removed from these conditions and grown in suspension, they begin to generate three-dimensional differentiating cell aggregates termed embryoid bodies (EBs). Two weeks after plating on gelatin coated plates, spontaneously contracting areas appear within the EBs. The Mummery protocol* [6], however, uses END-2 cells in the place of MEFs as feeders for hESCs; within 2 weeks, spontaneously contracting areas appear in the hESC-colonies. (hESCs: human Embryonic Stem Cells; MEFs: Mouse Embryo Fibroblasts; EBs: Embryoid Bodies; END2: visceral endoderm-like cells; CMCs: cardiomyocytes)