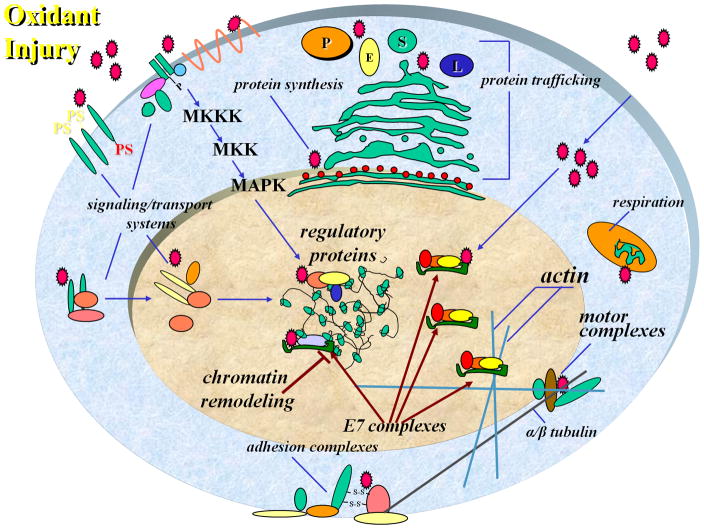
Fig. 5. Hypothetical mechanisms for the role of HPV E7 in control of the cellular response to redox-mediated injury and redox-dependent L1 reactivation.
Redox stress alters both cell signaling and transcription programs. Injury might lead either directly or indirectly to pRb/HDAC-dependent repression of factors required for LINE-1 silencing thus allowing for its reactivation. Cells expressing HPV E7 viral oncoprotein inactivate the Rb/HDAC effect, likely through direct interaction with Rb, thus eliminating the redox-mediated retroelement reactivation.