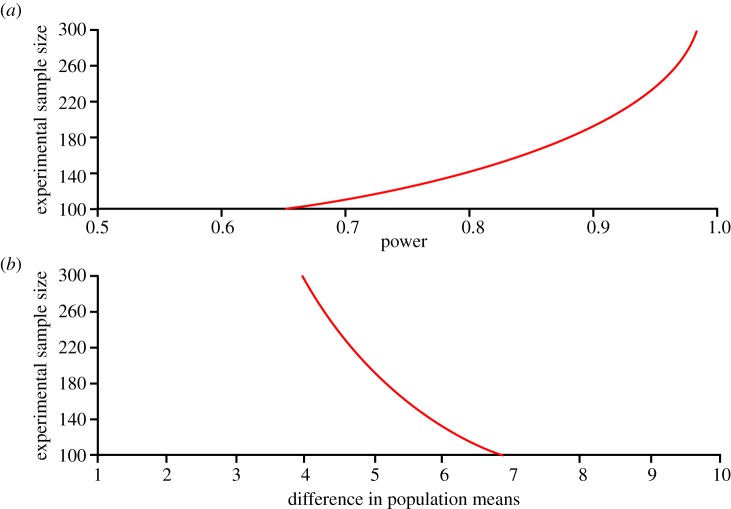
Figure 3.
Calculation of sample size for a randomized controlled trial to demonstrate the clinical benefit of cerebral oximetry in extremely preterm infants. It is hoped that the risk of brain injury can be reduced and it is expected that this will result in improved cognitive development. Calculations are based on an effect size of five points, corresponding to a Cohen d of 0.33, as the standard deviation of a test measuring cognitive function is 15 points, and a study power of 90%. It can be seen that 190 infants will be needed in each of the groups and that the groups must be even larger if the effect size is less, or if the study power should be higher. (Online version in colour.)