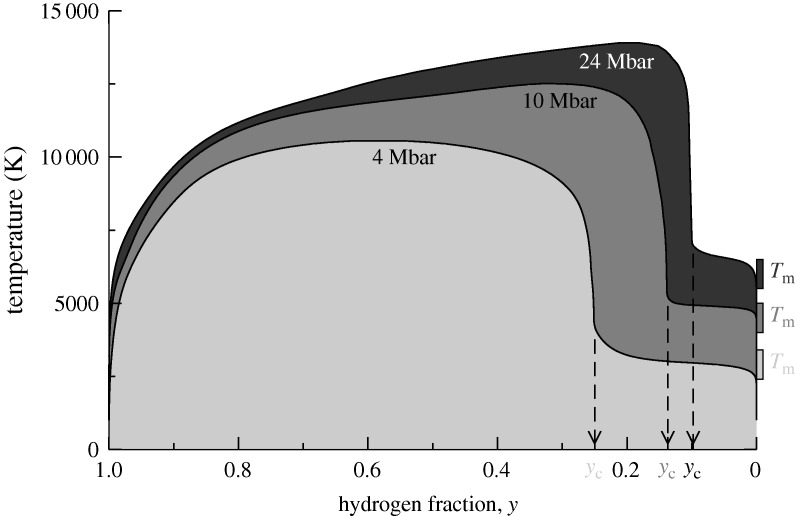
Figure 13.
Miscibility gap in the hydrogen–helium system for constant pressures as a function of the hydrogen concentration, y=NH/(NH+NHe) (see Lorenzen et al. 2009). The calculated melting temperatures, Tm, of solid helium are indicated on the right-hand side for each pressure. The strong increase in the demixing temperatures occurs at critical hydrogen concentrations yc, which are in accordance with Mott’s criterion, 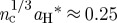 . We conclude that the thermodynamics that drives the phase separation in the mixture is caused by a continuous non-metal to metal transition in the hydrogen subsystem.
. We conclude that the thermodynamics that drives the phase separation in the mixture is caused by a continuous non-metal to metal transition in the hydrogen subsystem.