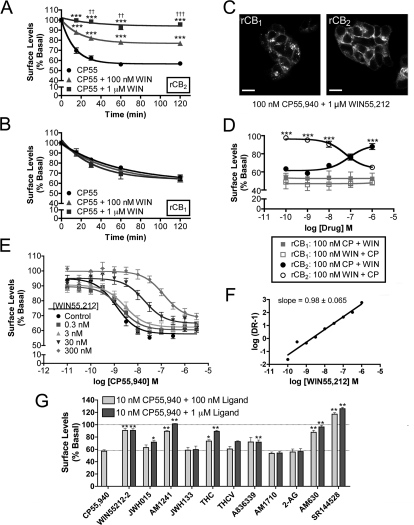
Fig. 3.
WIN55,212-2 and other aminoalkylindoles antagonize CP55,940-induced rCB2 internalization. A, time course of 100 nM CP55,940 (CP55)-induced internalization of rCB2 in HEK293 cells. Cotreatment with 100 nM CP55,940 and 1 μM WIN55,212-2 (WIN) attenuates CP55,940-mediated internalization. ***, p < 0.001 versus CP55,940 alone. ††, p < 0.01; †††, p < 0.001, 100 nM WIN55,212-2 versus 1 μM WIN55,212-2 (n = 4–6). B, WIN55,212-2 has no effect on CP55,940-mediated rCB1 internalization (n = 3–12). C, representative images of rCB1 and rCB2 HEK293 cells treated with the combination of 100 nM CP55,940 and 1 μM WIN55,212-2. Scale bars, 20 μm. D, rCB1 or rCB2 cells were cotreated with 100 nM CP55,940 (CP) and increasing concentrations of WIN55,212-2 (closed symbols) or alternatively cotreated with 100 nM WIN55,212-2 and increasing concentrations of CP55,940 (open symbols). ***, p < 0.001, CP + WIN versus WIN + CP (n = 3–15). E, individual concentration curves of CP55,940 with indicated concentrations of WIN55,212-2 cotreatments (n = 6–27). F, Schild plot constructed from data in E. The slope indicates that the interaction between CP55,940 and WIN55,212-2 is competitive. G, cotreatments of rCB2 HEK293 cells with 10 nM CP55,940 and 100 nM or 1 μM concentrations of the indicated ligands (n = 3–17). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01, versus CP55,940 alone. Data in A, B, and G analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparison test. Data in D analyzed using Student's t test.