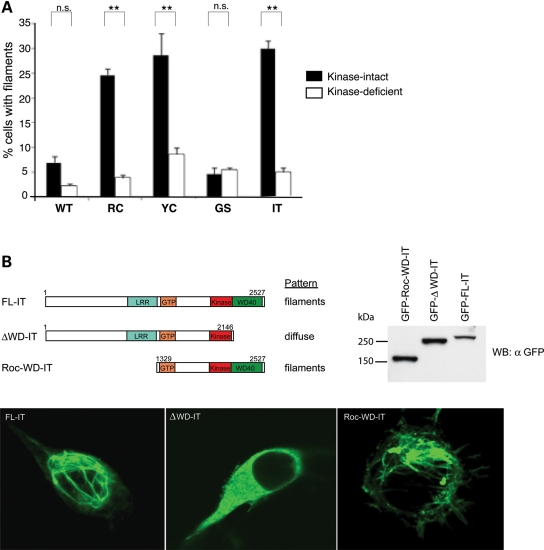
Figure 5.
Kinase activity and WD40 domain are required for LRRK2-microtubule association. (A) The microtubule-association effect of LRRK2 PD mutations is kinase-dependent. Blocking LRRK2 kinase function blocks the effect of filament formation caused by PD mutations. CAD cells were transfected with WT LRRK2-GFP or ‘double mutant’ constructs containing a LRRK2 PD mutation and a kinase-deficient mutation (K1906R) and stained for filaments with an anti-GFP antibody. Quantification of filament formation was done as in Figure 1E. Data are means ± SE of three independent experiments (**P< 0.01, n.s.: non-significant; ANOVA with Tukey's test). (B) Filament formation requires the WD40 domain of LRRK2. CAD cells were transfected with full-length GFP-LRRK2-I2020T (FL-IT), GFP-LRRK2-I2020T lacking the WD40 domain (ΔWD40) or the Roc and WD40 domains of LRRK2-I2020T (Roc-WD-IT). Forty-eight hours after transfection, the cells were assessed for filament formation. Anti-GFP immunoblot of transfected cell lysate demonstrates that truncated proteins are produced at the same or greater level of expression as full-length LRRK2.