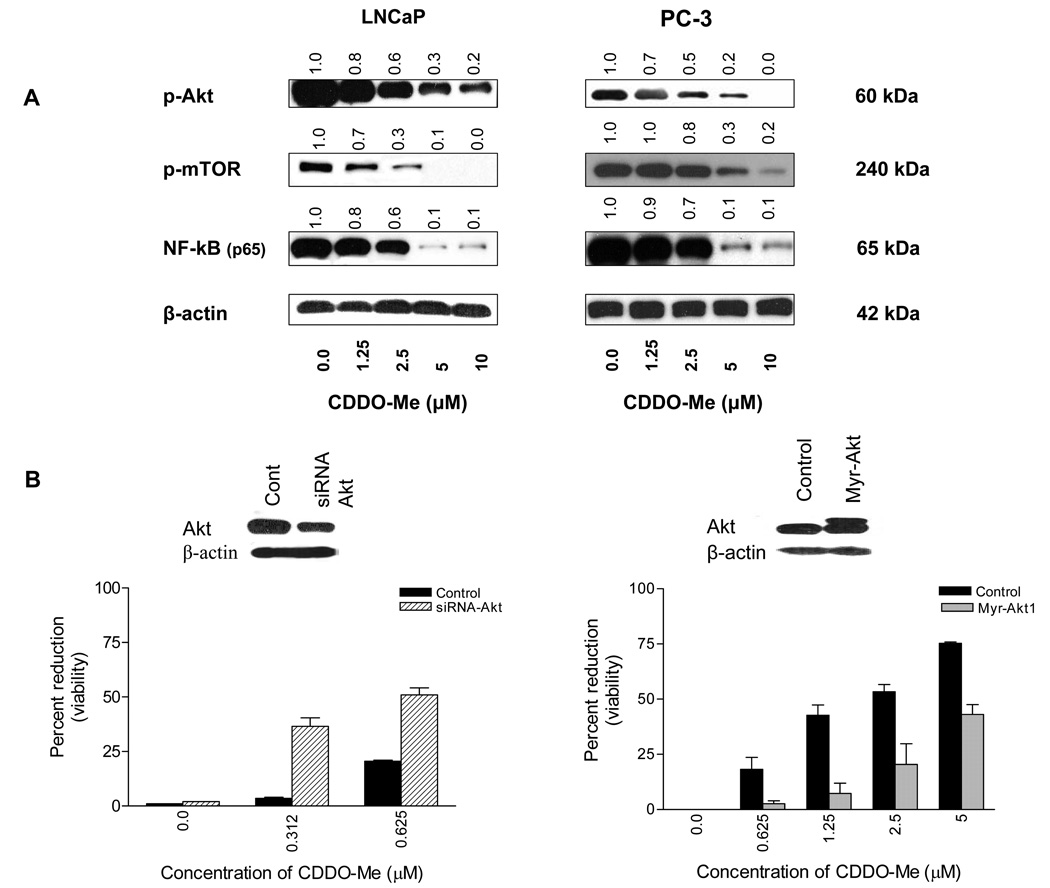
Figure 1. CDDO-Me inhibits p-Akt, p-mTOR and NF-κB (p65) and Akt determines the sensitivity of prostate cancer cells to CDDO-Me.
A. LNCaP and PC-3 cells were treated with CDDO-Me at concentrations of 1.25 to 10 µM for 20 h. After treatment, cell lysates were analyzed for p-Akt, p-mTOR, and NF-κB (p65) by western blotting. B. To determine the functional relevance of Akt in response to CDDO-Me, Akt expression was either inhibited or increased by transfecting PC-3 cells with siRNA-Akt or Akt1 expression plasmid (myr-Akt1-pUSE) using LipofectAMINE Plus reagent. The change in Akt expression levels was determined by western blotting (insets) and response of transfected cells to CDDO-Me was measured in MTS assay. Bar graphs represent mean ± SD of two separate experiments. Values above blots represent the change in protein expression level compared to untreated control represented as 1.0.