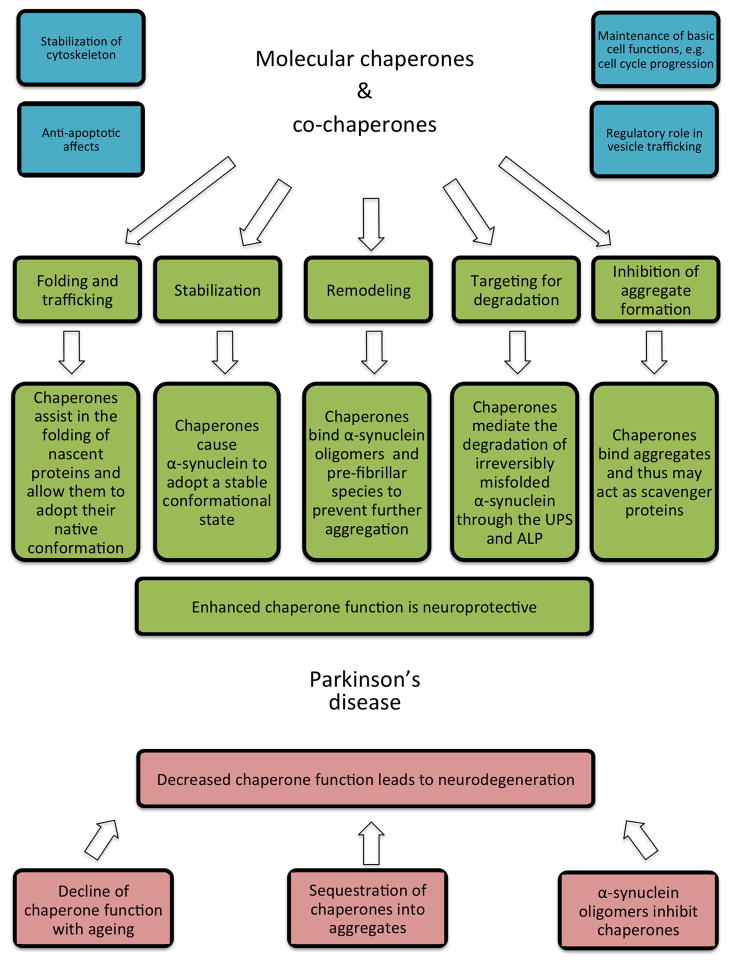
Figure 1.
Synopsis. The role of molecular chaperones in Parkinson’s disease can be summarized by two leading hypotheses: I) Molecular chaperones protect neurons against α-synuclein induced toxicity and II) Depletion of molecular chaperones exacerbates protein toxicity and neurodegeneration. Molecular chaperones are neuroprotective because of a myriad of actions that mitigate protein misfolding and aggregation. UPS (ubiquitin-proteasome system); ALP (autophagy-lysosomal pathway)