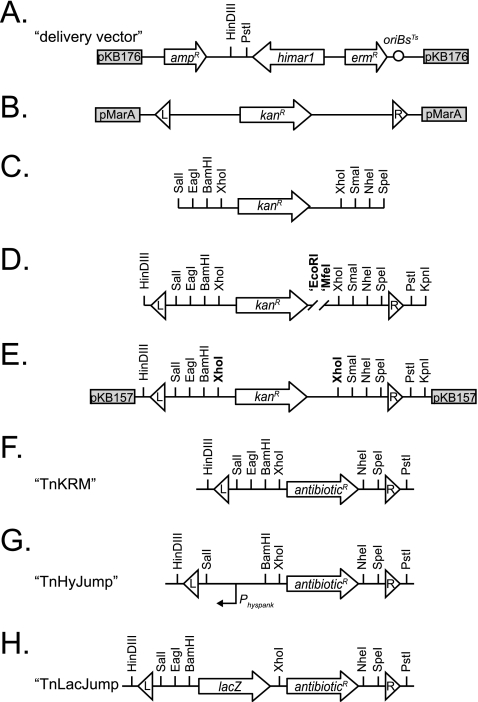
Fig 1.
Genetic maps of transposon construction and final architecture. (A) Map of the delivery vector pKB176, into which completed transposons are cloned and introduce to B. subtilis. (B to E) Maps of the intermediates in transposon assembly. All subsequent constructs were cloned into pKB157 as shown in panel E. (F to H) Generalized maps of the completed transposons for which the actual antibiotic resistance maker has been replaced by the term antibioticR. Arrows indicate genes. Boxes indicate the rest of the plasmid backbone and plasmid name. Circle indicates the temperature-sensitive origin of replication in B. subtilis [ori(TS)Bs]. Triangles indicate mariner insertion sequences (IS elements) labeled L (left) and R (right) to provide an arbitrary orientation. Vertical lines indicate restriction endonuclease sites. The bent arrow represents a promoter.