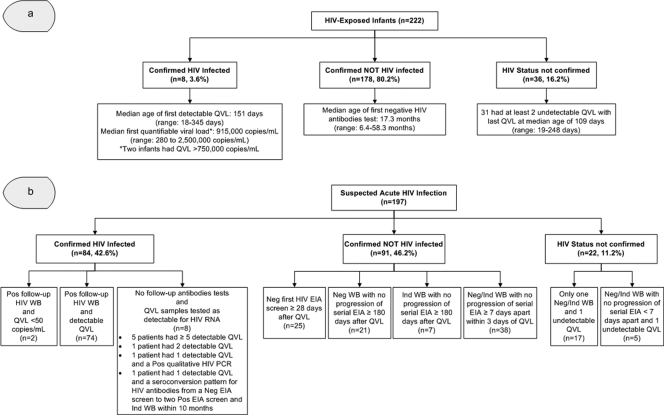
Fig 2.
Quantitative viral load results and serological follow-up for the two study populations in Central and Northern Alberta, HIV-exposed infants (a) and suspected acute HIV infections (b). (a) HIV-Exposed Infants, infants born to HIV-infected mothers between 1995 and 30 May 2009 in Central and Northern Alberta who were tested with QVL assays prior to 18 months of age; Confirmed HIV Infected, infants (<18 months of age) with ≥2 detectable QVL; Confirmed NOT HIV Infected, infants with all QVL samples tested as undetectable and a negative HIV antibody test on follow-up; HIV Status Not Confirmed, infants with all QVL samples tested as undetectable who were lost to follow-up with no follow-up HIV antibody test. (b) Suspected Acute HIV Infection, patients ≥2 years old with initial positive/indeterminate EIA screens and negative/indeterminate WBs between April 1996 and 30 April 2010 who had at least one detectable QVL within 150 days of their negative/indeterminate WB; Confirmed HIV Infected, patients with detectable QVL and/or a follow-up positive WB; Confirmed NOT HIV Infected, patients with all QVL samples tested as undetectable who failed to demonstrate progression/seroconversion on serial HIV antibody tests that were at least 7 days apart; HIV Status Not Confirmed, patients with all QVL samples tested as undetectable who had limited or no follow-up HIV antibody test. QVL, quantitative HIV RNA viral load; EIA, enzyme immunoassay; WB, Western blot; Pos, positive; Neg, negative; Ind, indeterminate.