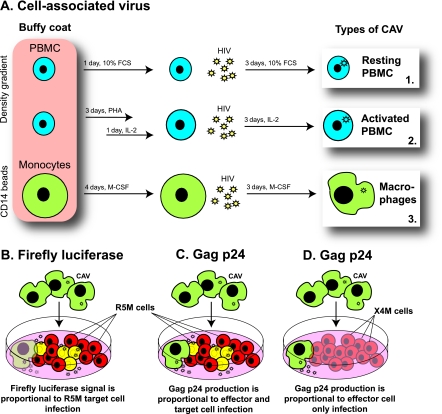
Fig 1.
Experimental setup. (A) In vitro generation of HIV-infected effector cells. Human PBMC were either activated with PHA and IL-2 or left untreated, while monocytes from the same donor were differentiated to macrophages. During the last 3 days of culture, all three cell types were infected with the R5-tropic subtype B strain BaL, resulting in three sources of HIV-infected effector cells: resting PBMC, activated PBMC, and macrophages. (B) Measuring infection of target cells. In a coculture of BaL-infected effector cells (green cells) with a firefly-luciferase-containing target T-cell line, R5M (red cells), luminescence originates only from infected R5M target cells (yellow cells). (C) Measuring infection of the coculture. In a coculture of BaL-infected effector cells with the HIV-permissive T-cell line R5M, the Gag p24 concentration in the supernatant quantifies the infection of both effector and target cells. (D) Measuring infection of effector cells. In a coculture of BaL-infected effector cells with the X4M T-cell line (blue cells), which lacks the coreceptor CCR5, the Gag p24 concentration in the supernatant quantifies the infection of the effector cells only, as the X4M cells do not become productively infected.