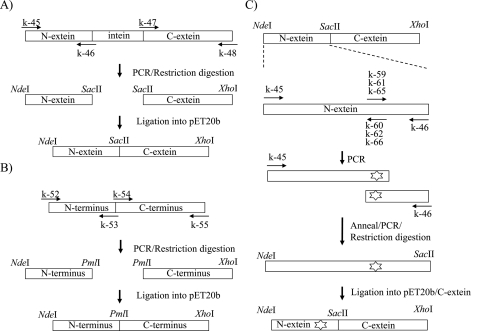
Fig 2.
Construction of WT and mutant DNA gyrase expression plasmid. (A) DNA fragments encoding N-extein (amino acids 1 to 130) and C-extein of GyrA (amino acids 125 to 830) were amplified by PCR with primer pairs k-45/k-46 and k-47/k-48 (Table 1), respectively. Similarly, those encoding the N-terminal (amino acids 1 to 428) and C-terminal (amino acids 424 to 679) regions of GyrB were amplified with primer pairs k-52/k-53 and k-54/k-55 (Table 1), respectively. PCR products encoding N-extein and C-extein of GyrA were digested by NdeI-SacII and SacII-XhoI, respectively, and introduced simultaneously into NdeI-XhoI-digested plasmid pET-20b (+). (B) DNA fragments encoding the N-terminal and C-terminal regions of GyrB were digested by NdeI-PmaCI and PmaCI-XhoI, respectively, and introduced into pET20b as described above. (C) Primer pairs consisting of primer k-45 and primer k-60, k-62, or k-66 (Table 1) were used for amplifying the DNA fragment encoding the N-terminal portion (amino acids 1 to 94) of N-extein carrying Ala91Val, Asp95Gly, and Asp95Asn, respectively. Primer pairs consisting of primer k-46 and primer k-59, k-61, or k-65 (Table 1) were used for amplifying the DNA fragment encoding the C-terminal portion (amino acids 88 to 130) of N-extein carrying Ala91Val, Asp95Gly, and Asp95Asn, respectively. To complete the N-extein-encoding cassette, DNA fragments encoding the N-terminal and C-terminal regions of N-extein of GyrA were annealed and reamplified by PCR using the primer pair k-45/k-46. The mutated gyrA-N cassettes were digested with NdeI and SacII restriction endonucleases and ligated into the expression plasmid containing WT gyrA C-extein DNA fragment digested by the same enzymes.