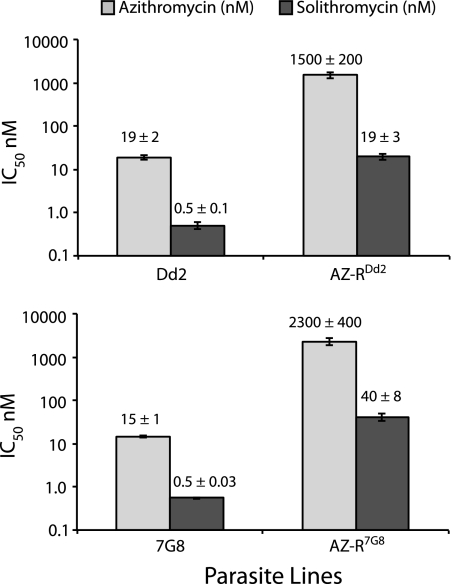
Fig 1.
Solithromycin exhibits activity against multidrug-resistant parasites. Two multidrug-resistant parasite lines, Dd2 and 7G8, and azithromycin-resistant clones derived from these parental lines, AZ-RDd2 and AZ-R7G8, were treated with the indicated compounds for 96 h. Solithromycin was significantly more potent than azithromycin for both the sensitive and resistant lines: Dd2, P = 0.004; AZ-RDd2, P = 0.007; 7G8, P = 0.0005; and AZ-R7G8, P = 0.01, all by paired t tests. Azithromycin-resistant parasites were significantly less susceptible to solithromycin than the parental strains (P < 0.05 for both lines), but this effect was only about 50% as great as the effect for azithromycin itself (for Dd2 versus AZ-RDd2 there was an 80- and 40-fold shift in potency for azithromycin and solithromycin, respectively; for 7G8 versus AZ-R7G8 there was a 160- and 70-fold shift in potency for azithromycin and solithromycin, respectively. IC50s (means ± SEM) for each line tested against azithromycin or solithromycin are shown above the individual bars (data were obtained from four independent experiments performed in duplicate).