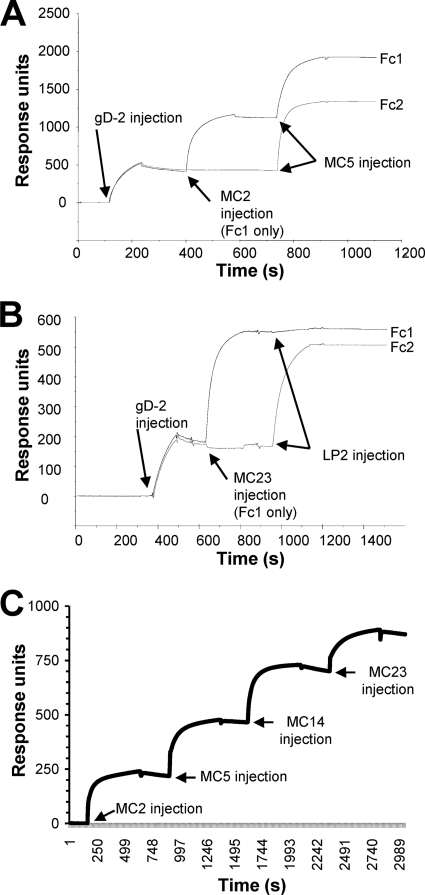
Fig 3.
MAb blocking of gD binding to receptors measured by surface plasmon resonance. Anti-His MAb was coupled to a CM5 biosensor chip, and gD2(306t) was captured via its C-terminal His tag on flow cell 1 (Fc1) and Fc2. The first MAb was injected across Fc1 for 2 min at 5 μl/min (control flow cell). The next MAb was then injected across both Fc1 and Fc2 for 2 min. (A) Sensorgram obtained using MAbs MC2 (1st MAb) and MC5 (2nd MAb). Since both bind to gD, there was no competition. (B) Sensorgram obtained using MC23 (1st MAb) and LP2 (2nd MAb). In this case, when MC23 was injected first, LP2 failed to bind, indicating they competed for the same epitope on gD. (C) Sensorgram of MC2, MC5, MC14, and MC23, each added sequentially to gD in Fc1. Binding of gD2(306t) to the anti-His MAb is not shown. In this case, each MAb bound to gD independently of whether the other MAbs were present, indicating that all four recognize distinct epitopes on gD.