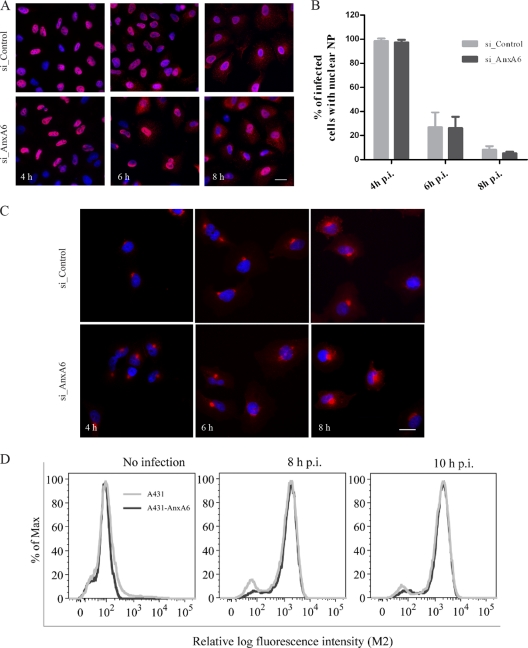
Fig 5.
AnxA6 does not affect vRNP export or M2 protein expression and trafficking. (A and B) NP subcellular localization in AnxA6-depleted A549 cells. A549 cells treated with the indicated siRNAs were infected with influenza A/WSN/33 virus at an MOI of 5. Cells were fixed at 4, 6, and 8 h p.i. for immunostaining of NP as a marker for vRNP complex export, and nuclei were stained using DAPI. Bar, 20 μm. Cytoplasmic and nuclear NP localization was quantified using Metamorph software, and the plotted histogram represents the percentage of infected cells with nuclear NP only. Data are shown as means ± SD for measurements from at least 200 cells in duplicates of a representative experiment. (C) M2 subcellular localization in AnxA6-depleted A549 cells. A549 cells treated with the indicated siRNAs were infected with influenza A/WSN/33 virus at an MOI of 5. Cells were fixed at 4, 6, and 8 h p.i. for immunostaining of M2 protein. Bar, 20 μm. (D) AnxA6 overexpression does not affect M2 cell surface expression. A431 cells and the A431-AnxA6 stable cell line were infected with influenza A/WSN/33 virus at an MOI of 3. Cells were fixed at 8 and 10 h p.i., left nonpermeabilized, and labeled with mouse anti-M2 MAb followed by Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG for M2 cell surface analysis by flow cytometry. The graph shows the amount of cell surface expression and fluorescence intensity of the M2 viral antigen.