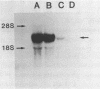
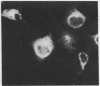
Abstract
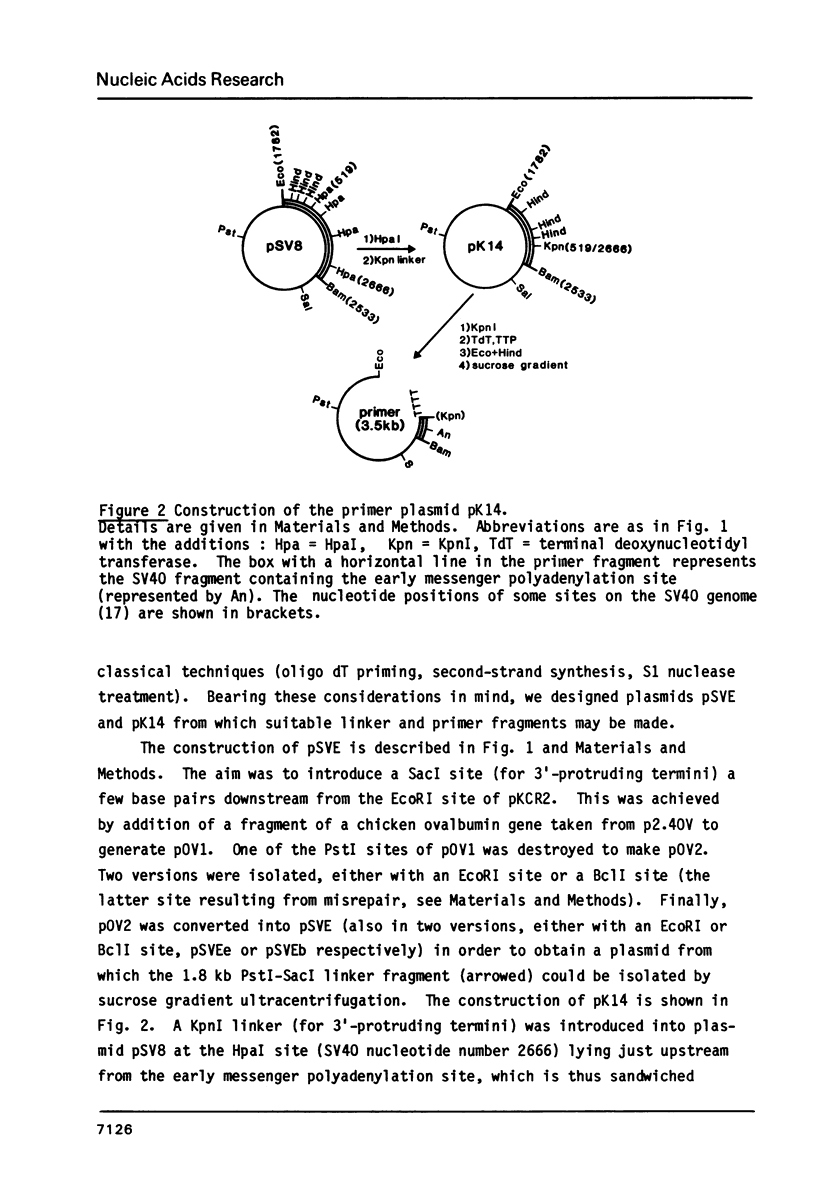
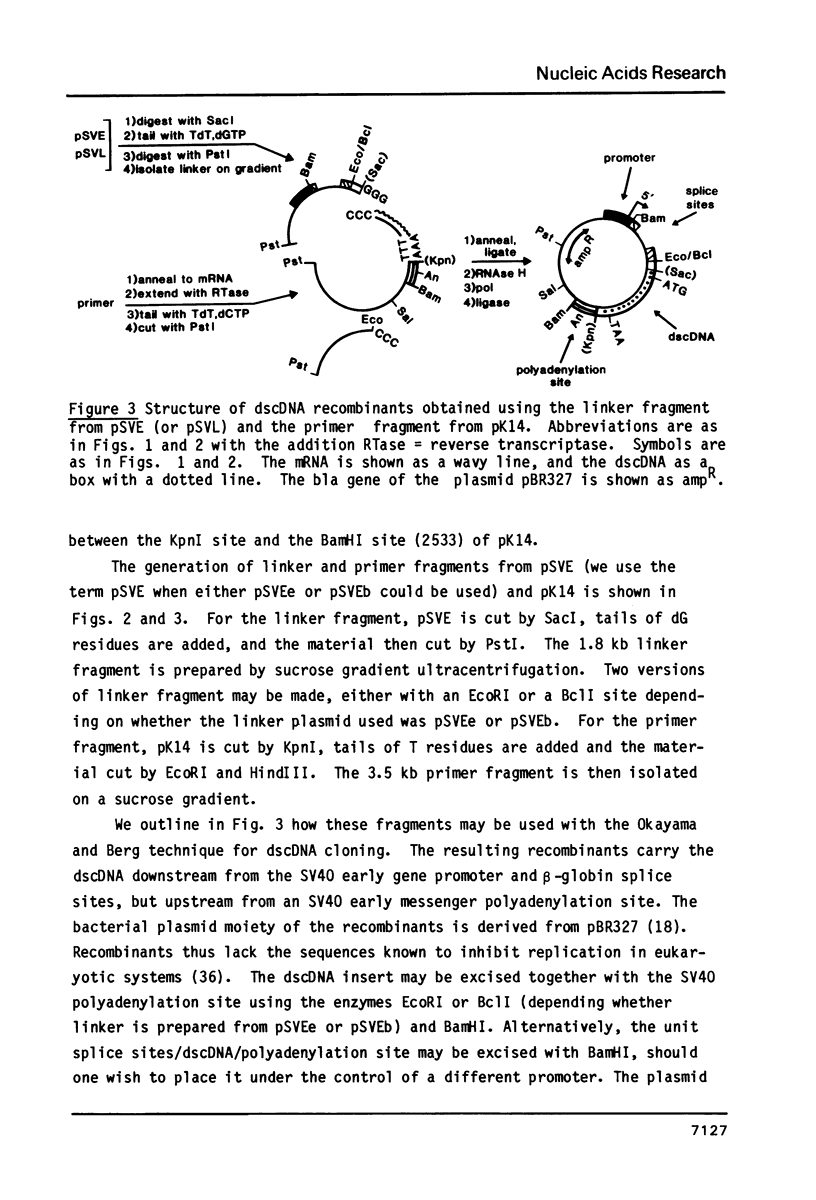
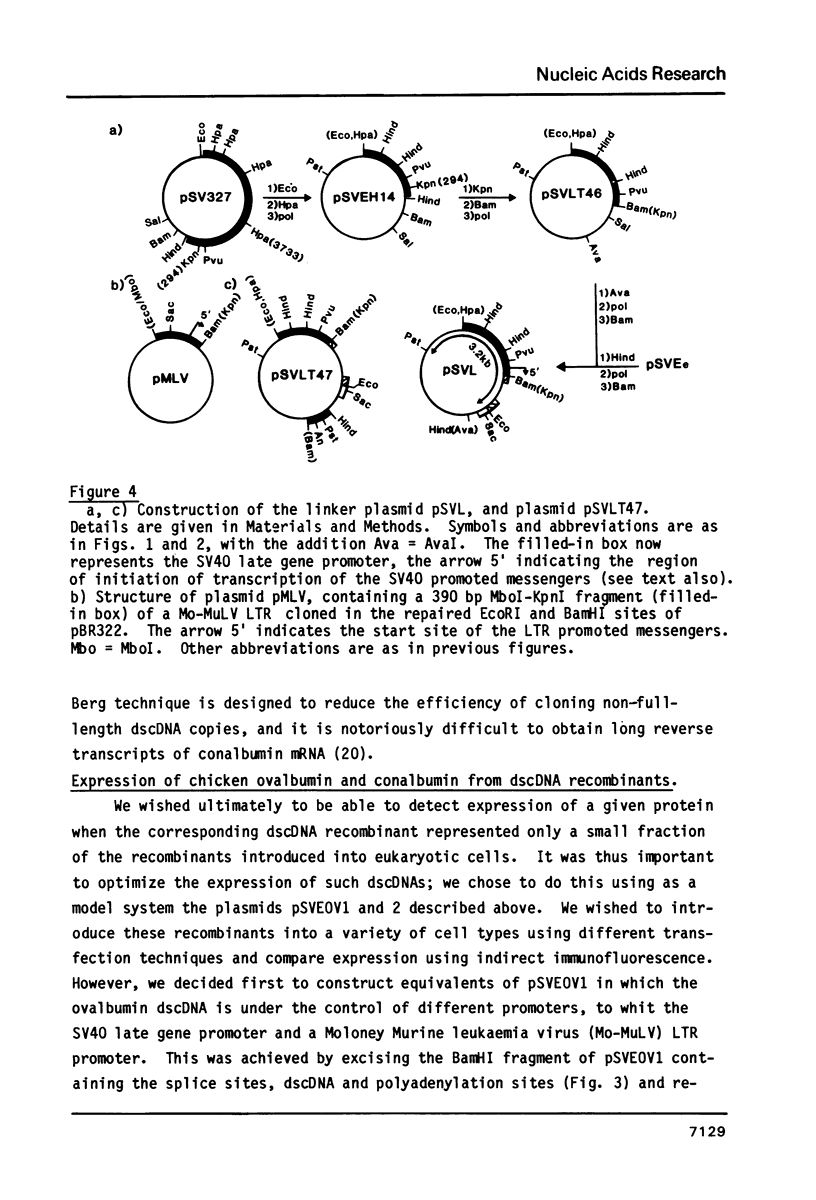
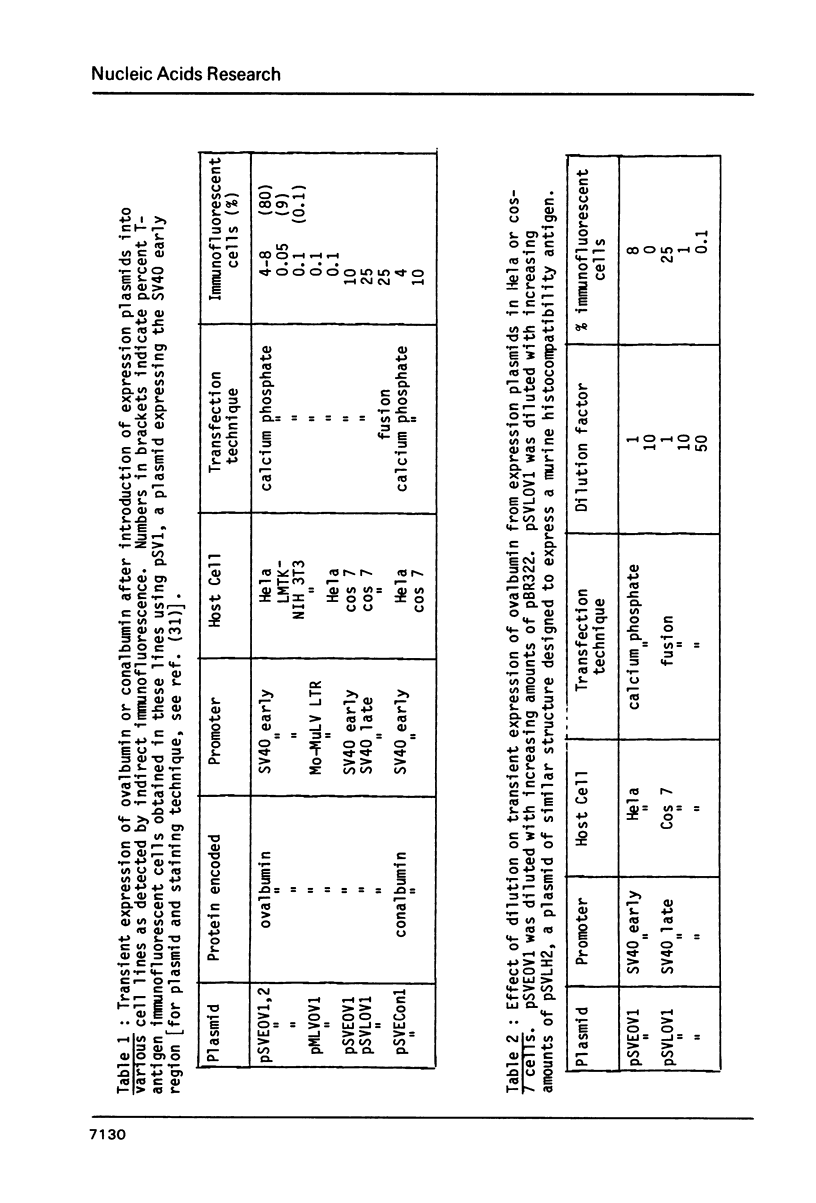
Okayama and Berg (1) have recently described a technique for the high efficiency cloning of full-length dscDNAs. We have constructed eukaryotic expression vectors compatible both with this technique (and with classical techniques) for dscDNA cloning. The vectors are such that recombinants obtained contain dscDNAs in the correct orientation downstream from a block of sequence comprising either the SV40 early or late gene promoter linked to a pair of splice sites from a rabbit beta-globin gene. A sequence encoding an SV40 polyadenylation site follows the dscDNA. We have used our vectors to make a library from chicken oviduct polyA(+) RNA using the Okayama and Berg technique. Ovalbumin recombinants occur in the library at the expected frequency and a high proportion contain full length copies of the ovalbumin mRNA. However, a similar result was not obtained for conalbumin recombinants. When recombinants are introduced into eukaryotic cells by either calcium phosphate coprecipitation or protoplast fusion, expression of chicken ovalbumin or conalbumin may be detected by indirect immunofluorescence. Under optimal conditions (use of SV40 late promoter and cos 7 cells) ovalbumin protein could be detected when the ovalbumin recombinant was present in only 2% of the protoplasts used for fusion. This suggests that colony banks obtained using our vectors could be screened in batches of 50 by protoplast fusion followed by a search for expression of a given protein using indirect immunofluorescence.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Mandel J. L., Chambon P. Ovalbumin gene is split in chicken DNA. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):314–319. doi: 10.1038/270314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Mantei N., Chambon P. Corrected splicing of a chicken ovalbumin gene transcript in mouse L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):740–744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buell G. N., Wickens M. P., Payvar F., Schimke R. T. Synthesis of full length cDNAs from four partially purified oviduct mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2471–2482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corsaro C. M., Pearson M. L. Enhancing the efficiency of DNA-mediated gene transfer in mammalian cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Sep;7(5):603–616. doi: 10.1007/BF01549662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gheysen D., Fiers W. Expression and excretion of human fibroblast beta 1 interferon in monkey cells after transfection with a recombinant SV40 plasmid vector. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):385–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Feramisco J. R., Fiddes J. C., Thomas G. P., Hughes S. H. Identification of clones that encode chicken tropomyosin by direct immunological screening of a cDNA expression library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):31–35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries P., Cochet M., Krust A., Gerlinger P., Kourilsky P., Chambon P. Molecular cloning of extensive sequences of the in vitro synthesized chicken ovalbumin structural gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jul;4(7):2389–2406. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.7.2389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolly D. J., Okayama H., Berg P., Esty A. C., Filpula D., Bohlen P., Johnson G. G., Shively J. E., Hunkapillar T., Friedmann T. Isolation and characterization of a full-length expressible cDNA for human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):477–481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Grez M., Hauser H., Lindenmaier W., Schütz G. 5'-Terminal sequences of eucaryotic mRNA can be cloned with high efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2251–2266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masiakowski P., Breathnach R., Bloch J., Gannon F., Krust A., Chambon P. Cloning of cDNA sequences of hormone-regulated genes from the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):7895–7903. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.7895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Expression of a bacterial gene in mammalian cells. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1422–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.6251549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare K., Benoist C., Breathnach R. Transformation of mouse fibroblasts to methotrexate resistance by a recombinant plasmid expressing a prokaryotic dihydrofolate reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1527–1531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin F., Cochet M., Gerlinger P., Cami B., LePennec J. P., Chambon P. The chicken conalbumin gene: studies of the organization of cloned DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 25;6(8):2731–2748. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.8.2731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Goldfarb M., Shimizu K., Lama C., Fogh J., Wigler M. Human-tumor-derived cell lines contain common and different transforming genes. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):467–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90388-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassoulzadegan M., Binetruy B., Cuzin F. High frequency of gene transfer after fusion between bacteria and eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):257–259. doi: 10.1038/295257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W. Direct transfer of cloned genes from bacteria to mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2163–2167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. D., Boll W., Taira H., Mantei N., Lengyel P., Weissmann C. Structure and expression of cloned murine IFN-alpha genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):555–573. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberon X., Covarrubias L., Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. IV. Deletion derivatives of pBR322 and pBR325. Gene. 1980 May;9(3-4):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90328-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Matsui H., Fujita T., Takaoka C., Kashima N., Yoshimoto R., Hamuro J. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for human interleukin-2. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):305–310. doi: 10.1038/302305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., Rands E., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Verma I. M. Long terminal repeat of murine retroviral DNAs: sequence analysis, host-proviral junctions, and preintegration site. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):542–556. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.542-556.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Olson L., Tyndall C., Schaffner W. Transcriptional 'enhancers' from SV40 and polyoma virus show a cell type preference. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):7965–7976. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.7965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]