Figure 2.
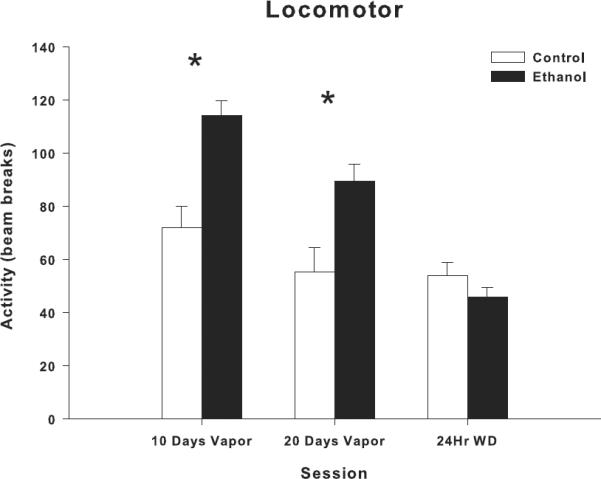
Effects of adolescent ethanol vapor exposure on locomotor behavior. Ethanol-exposed rats (n=24) showed a significant increase in locomotor activity at both PD 32 (10 days of vapor exposure) and PD 42–44 (20 days of vapor exposure), compared to controls (n=12). Ethanol-exposed and control rats showed no difference in locomotor activity levels 24 hrs after the final withdrawal from ethanol vapor exposure. Locomotor behavior is expressed as activity obtained by quantifying beam breaks. * indicates P< 0.05 for significant difference from control rats. Error bars=S.E.M.
