Figure 2.4.
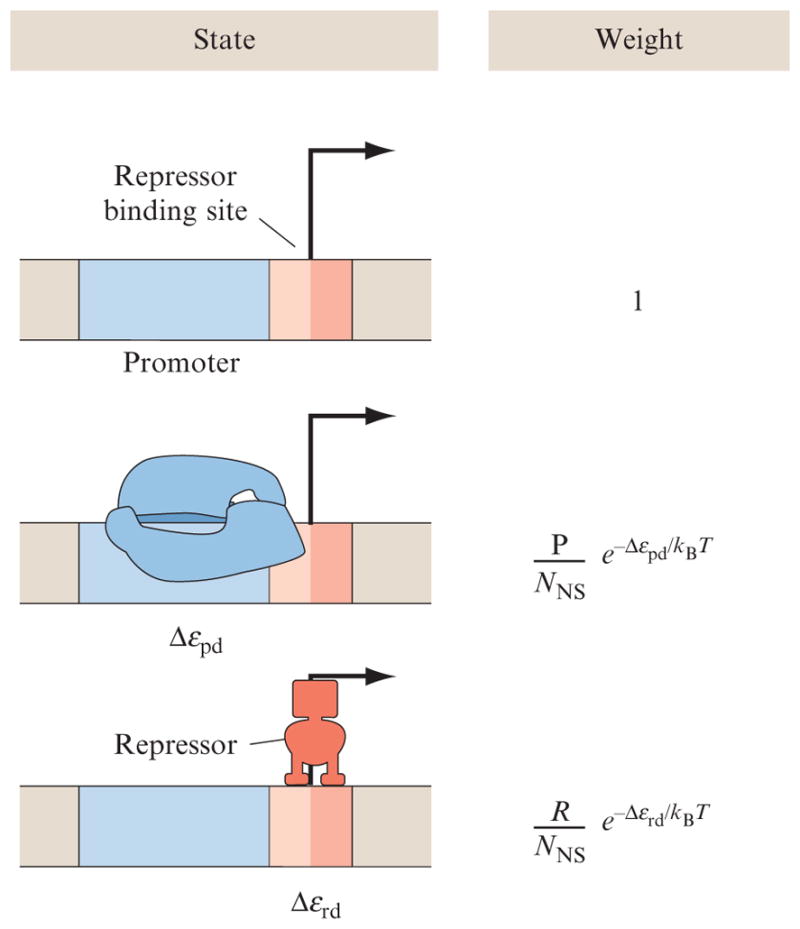
States and weights for simple repression. A promoter has a binding site for a repressor molecule which excludes the binding of RNA polymerase. The statistical weights of the different states depend upon the number of polymerases (P), the number of repressors (R), and their respective energies of binding to DNA, Δεpd, and Δεrd. To derive these weights, we use the same approach as that described for ligand–receptor binding, except now we assume that both polymerases and repressors when not bound to the promoter are distributed among NNS sites on the bacterial genome (this is essentially the size of the genome). The energies in the Boltzmann factors are computed as the difference between the energy when repressor or polymerase is bound specifically to the promoter region of the DNA and when they are bound nonspecifically somewhere else on the genome (Bintu et al., 2005b).
