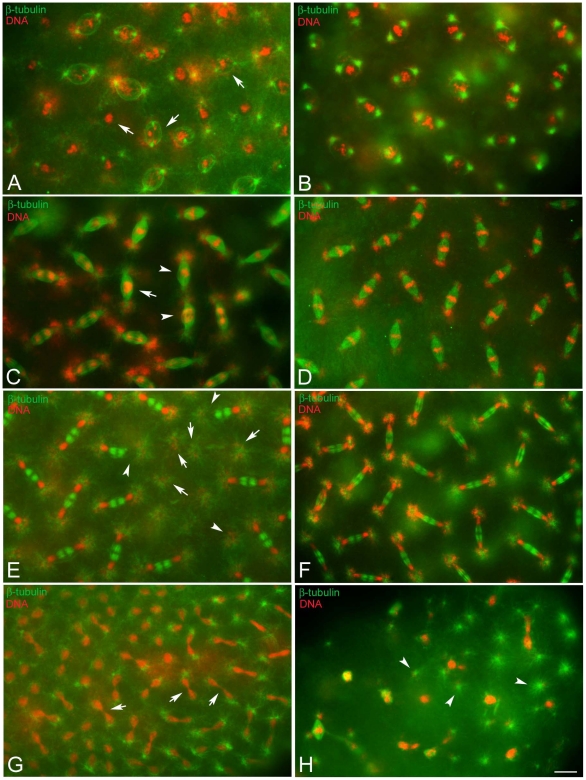
Figure 3. Defects of chromatin condensation and spindle organization during the syncytial blastoderm mitoses.
Eggs fixed during the syncytial blastoderm stage and incubated with antibodies against β-tubulin (green), acetylated-α-tubulin (blue), and counterstained with Hoechst 33258 (red). (A,B) Prophase, (C,D) metaphase/anaphase, (E,F) telophase of the tenth nuclear division cycle: chromosomes have condensation defects (arrows in A, C) or do not migrate properly (arrowheads in C); telophase spindles without nuclei (arrows in E) or with only one daughter (arrowheads in E) are seen; although the poles of these spindles lack nuclei they have large asters to which bacteria are associated. (G) Detail of the anterior pole of an embryo during late telophase of the eleventh nuclear division cycle showing marked chromatin bridges (arrows). (H) Detail of an abnormal embryo showing irregular chromatin masses and free centrosomes (arrowheads). Scale bar is 4 µm.