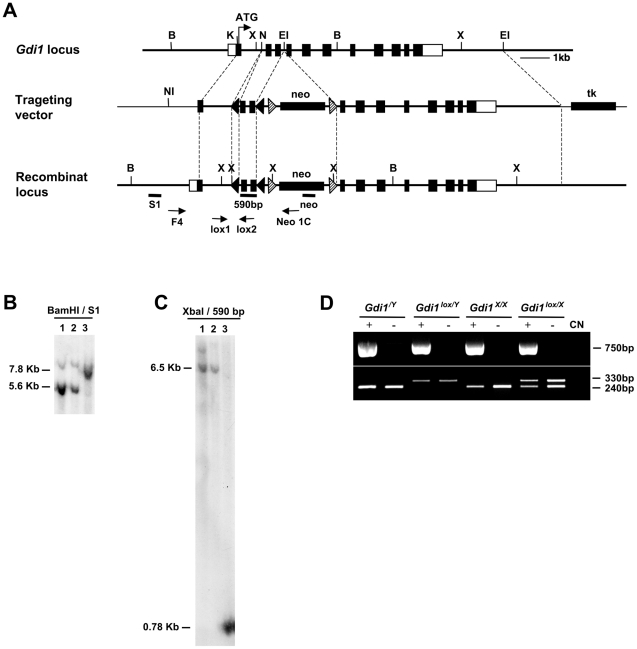
Figure 1. Gene targeting and generation of Gdi1flox/Y mice.
(A) Scheme of the structural organization of the Gdi1 gene (top), of the targeting vector (middle) and of the recombinant locus (bottom). Black boxes are coding exons or the indicated insertion cassettes; white boxes are 5′ and 3′ UTR regions. Restriction enzymes are BamHI (B), XbaI (X), NotI (NI), EcoRI (EI), NdeI (N) and KpnI (K). The position of the PCR primers for the screening of the G-418 resistant embryonic stems cell clones (F4; Neo1C) and for mice screening (Lox1; Lox2) are indicated by arrows. S1, neo and 590 bp are the probes for Southern blot analysis. (B–C) Southern blot analysis of the embryonic stem cell clone found positive by PCR (lane 3), compared with negative clones (lane 1–2). (B) Genomic DNAs were digested with BamHI, fractionated on agarose gel and hybridized with the probe 5′ S1 probe. The 5.6 Kb BamHI fragment corresponds to the wild type locus, the 7.8 Kb fragment to the recombinant locus, with neo insertion. (C) Genomic DNAs were digested with XbaI, fractionated on agarose gel and hybridized with the 590 bp probe, corresponding to the fragment cloned between lox P sites. The 6.5 kb XbaI fragment corresponds to the wild type locus and the 0.780 Kb fragment to the recombinant locus with the insertion of lox P sites. (D) PCR analysis of DNA extracted from the tails of mice, using the primers Lox1/Lox2 (330 bp correspond to the lox allele and 240 bp to the WT) and Cre1/Cre2 (750 bp correspond to the presence of the CaMKII-Cre-159 transgene).