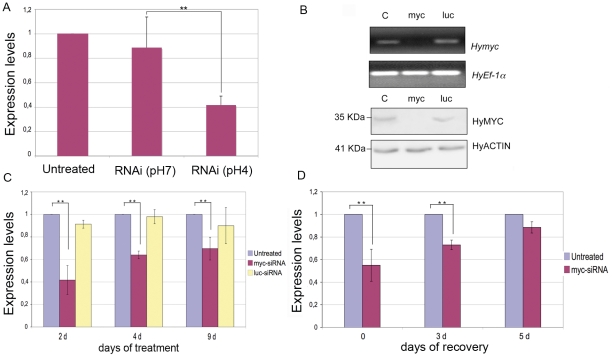
Figure 2. Molecular characterization of Hymyc1 RNAi.
(A) quantitative RT-PCR showing Hymyc1 downregulation enhanced by acidic condition. Animals treated by myc-siRNA at pH 4 showed 60% decrease in Hymyc1 transcription levels compared to Hydra Elongation factor HyEF1α mRNA, used as internal control (two asterisks, p<0.01 according to t-Student test). (B) Upper panel: semi-quantitative RT-PCR showing Hymyc1 downregulation induced specifically by myc-siRNA (lane myc) and not by luc-siRNA (lane luc), or in untreated animals (lane C) used as controls. Lower panel: Hymyc1 RNAi affects also MYC protein levels. Lane labels are as in the upper panel. MYC protein levels were detected using anti-HyMYC1 antibody (1∶500, kindly provided by K.Bister, University of Innsbruck) and compared to actin proteins, using an anti-actin primary antibody (1∶100, Sigma) to probe an identical blotted gel. HyMYC1 shows an apparent mol. weight of 35 kDa, as elsewhere reported [10]. (C) Kinetics of Hymyc1 downregulation. qRT-PCR was performed on total RNA extracted from 25 animals either untreated (namely incubated at pH 4, in absence of siRNA) or incubated with the indicated siRNA for different periods. The most effective downregulation is detected at the beginning of the treatment, and it is specifically induced by myc- and not luc-siRNA duplexes (two asterisks, p<0.01 according to t-Student test). (D) Reversible effect of RNAi. Animals were treated with myc-siRNA for 4 d (time t = 0) and then cultured in physiological condition for the indicated periods of time (3 days, 5 days), when total RNAs were extracted for qRT-PCR analysis. Suspension of RNAi treatment restored in five days myc mRNA transcript levels up to physiological values. Error bars in A, C and D indicate standard deviations calculated from three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate.