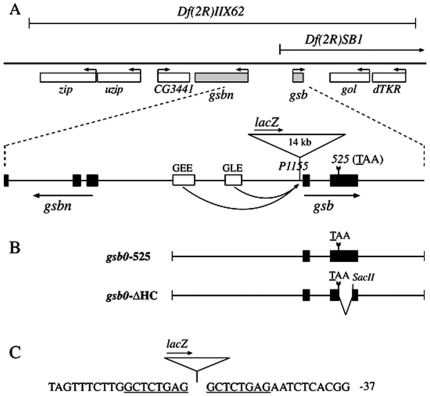
Figure 1. Locus of the gsb gene.
(A) gsb mutant alleles. The two deficiencies, Df(2R)IIX62 and Df(2R)SB1, as well as the two hypomorphic alleles, gsb525 and gsbP1155, are depicted. Neighboring genes uncovered by Df(2R)IIX62, zip, uzip, CG3441, and gsbn upstream of gsb, gol and dTKR downstream of gsb, and their direction of transcription are indicated (the rigth telomere of the second chromosome is to the right). Exons are marked by black boxes in the enlarged portion of (A) and also in (B). (B) Map of gsb0-525 abd gsb0-ΔHC transgenes. Both transgenes contain the upstream epidermis enhancers of gsb, GEE and GLE ( Fig. 1A ; Li et al., 1993), the gsb promoter, and the entire 3′ UTR of gsb. In gsb0-ΔHC, 519 bp of coding region between the gsb525 mutation and a SacII site are deleted, resulting in a shift of the open reading frame after the gsb525 nonsense mutation. (C) Sequence surrounding the gsbP1155 insertion site. The negative numbers refer to nucleotides upstream of the transcription start site. The eight nucleotides, duplicated during insertion of the P-element, are underlined.