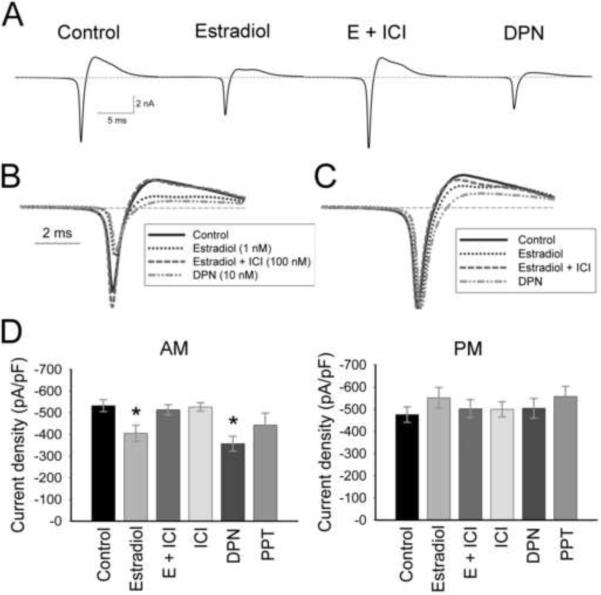
Figure 4.
The effects of estradiol on AM sodium current amplitude are mediated through ERβ. (A) Representative AM traces (average of 10 records) from cells of similar capacitance (11–12 pF) incubated in ACSF (control), 1 nM estradiol, 1 nM estradiol + 100 nM ICI 182,780 (E + ICI), or 10 nM DPN. Traces are overlaid in B, and normalized to peak current in C. Note the shift in time of peak current in estradiol- and DPN-treated cells compared to currents in control cells. (D) Mean current amplitude in AM recordings is significantly reduced in estradiol-treated and DPN-treated neurons (*, p ≤ 0.03 compared to control, E + ICI, or ICI). The ERα agonist PPT did not significantly reduce AM currents (p = 0.12). No estrogen receptor agonists or antagonists modulated currents from PM recordings (p = 0.67). n = 25 for control cells, 10–15 for treated cells.