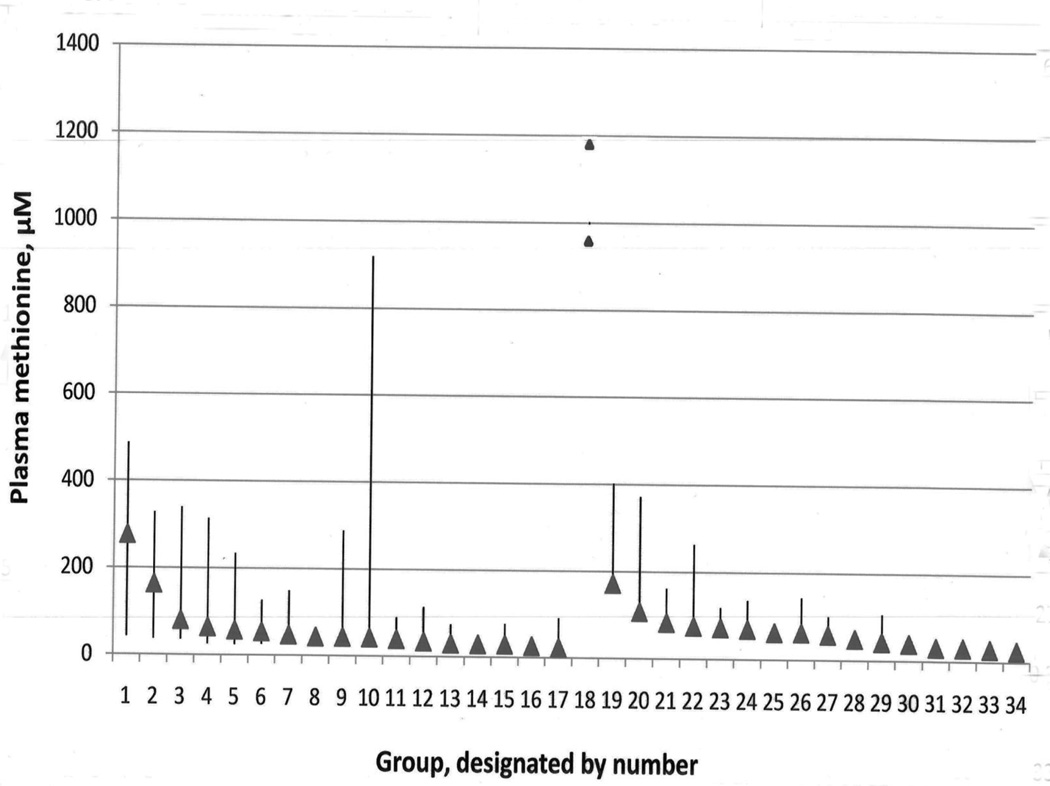
Figure 4.
Plasma methionine concentrations in the two patients reported in this paper with proven mitochondrial disorders, and in 33 groups of patients with liver disease (taken from previous publications). Peak values for the two mitochondrial disorder patients are indicated by the triangles placed in position 18 between groups 17 and 19 because these patients are not members of any of the 33 groups with liver disease. The reference range for the laboratory in which plasma methionines for these two patients were assayed is 13.3 to 42.7 µM. For each group of liver disease patients the mean is indicated by a triangle. Groups 1–17 are arranged from left to right according to descending values of their means with the vertical bars indicating the overall range for each group. Patient groups 19–34 are similarly arranged by descending means, but the vertical bars represent means + 2 SD because overall ranges for these groups were not reported. A total of 777 patients are included in the combined groups with liver diseases. The patient groups used are the following: 1. Deep hepatic coma [59]; 2. Hepatic precoma [59]; 3. Cryptogenic cirrhosis [60]; 4. Cirrhosis [61]; 5. Chronic active hepatitis with progression to cirrhosis [60]; 6. Viral hepatitis [60]; 7. Primary biliary cirrhosis [60]; 8. Severe cirrhosis, Child-Pugh class B/C[62]; 9. Decompensated cirrhosis [63]; 10. Alcoholic hepatitis with or without cirrhosis [60]; 11. Hepatitis [22]; 12. Alcoholic fatty liver: [60]; 13. Alcoholic hepatitis [64]; 14. Mild cirrhosis, Child-Pugh class A [62]; 15. Alcoholic liver disease [28]; 16. Compensated cirrhosis [63]; 17. Chronic persistent/active hepatitis [63]; 18. Patients 1 and 2 with proven mitochondrial abnormalities. 19. Acute hepatic necrosis/encephalopathy [65]; 20. Extrahepatic biliary atresia and cirrhosis [66] 21. Cirrhosis with coma [67]; 22. Cirrhosis, Child-Pugh C. [67]; 23. Chronic cirrhosis/encephalopathy [65]; 24. Cirrhosis, Child-Pugh B or C [68]; 25. Micronodular alcoholic cirrhosis [69]; 26. Alcoholic cirrhosis [70]; 27. Alcoholic cirrhosis [71]; 28. Alcoholic cirrhosis [72]; 29. Cirrhosis, Child-Pugh B. [67]; 30. Chronic cirrhosis [65] 31. Hepatitis [67]; 32. Cirrhosis, Child-Pugh A [67]; 33. Inactive cirrhosis:[73]; 34. Fatty liver [67].