Figure 1. The effects of the interaction of Neuroticism (N) by Acculturation (A) by Time on the Cortisol Awakening Response (CAR) in Mexican Americans.
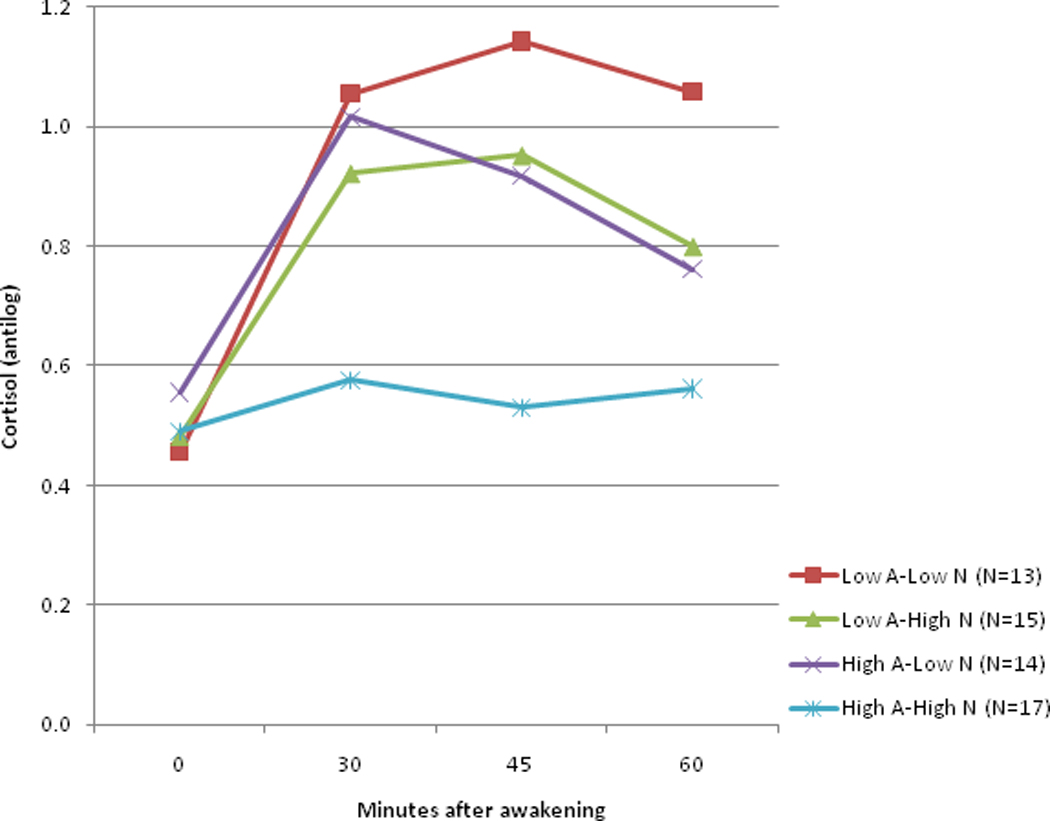
The effects of the Time × Neuroticism × Acculturation interaction on the Cortisol Awakening Response (CAR). The three-factor Neuroticism by Acculturation by Time interaction was significant (p = 0.0026) when the Neuroticism and Acculturation scales were included as dimensional covariates. To display the result, Neuroticism and Acculturation scales were split at their means to create dichotomous indicators (low, high), and the data reanalyzed using these classifications in a 2 (Neuroticism) × 2 (Acculturation) × 4 (Time) mixed effects regression model. Participants who were low on both dimensions had a greater CAR (a test of change over time in this group yielded (F = 14.75, df = 3,162, p<0.0001). In contrast, greater neuroticism was associated with an attenuated CAR in highly acculturated Mexican Americans with greater Anglo orientation (test for change over time yielded (F =1.07, df = 3, 162, p = 0.36). The graphic displays the exponentiated means of the log-transformed data (antilogs are presented to put the data in its original scale).
