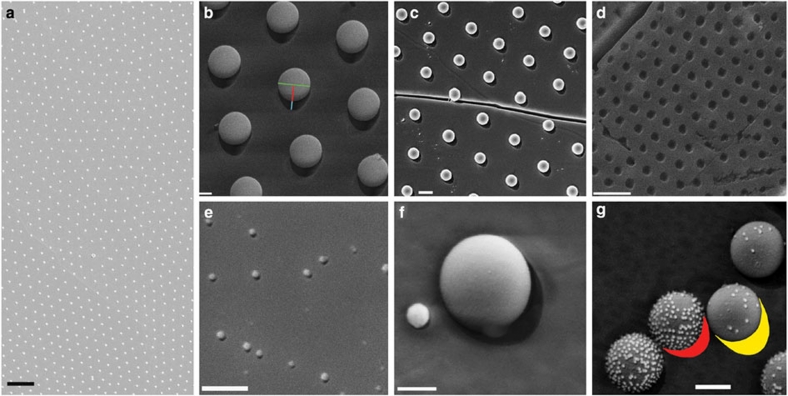
Figure 3. Cryo-SEM images of different NPs at the liquid–liquid interface after freeze-fracture.
The shadow cast by the nanoparticles (NPs) on metal deposition is visible in the high-magnification images. (a) Low-magnification image of 200 nm amidine latex particles at the n-decane/water interface. Scale bar, 3 μm. (b) 500 nm amidine latex particles at the n-decane/water interface. The key quantities necessary to measure the contact angle are highlighted for one particle: particle diameter (green), projected height l (red+cyan) and shadow length k (cyan). Scale bar, 200 nm. (c) 200 nm amidine latex particles at the water/n-hexane interface. A further fracture line in the ice is visible. Scale bar, 300 nm. (d) Hollow prints left by 500 nm amidine latex particles in the frozen n-decane side of the interface. Scale bar, 2 μm. (e) 20 nm amidine latex particles at the n-decane/water interface. Scale bar, 200 nm. (f) 100 nm hydrophilic citrate gold NP next to a 500 nm amidine latex NP at the water/n-decane interface. Scale bar, 200 nm. (g) 500 nm amidine latex NPs coated by 20 nm citrate gold NPs at the water/n-decane interface. Higher surface coverage of gold NPs renders the larger colloids more hydrophilic. Scale bar, 300 nm.