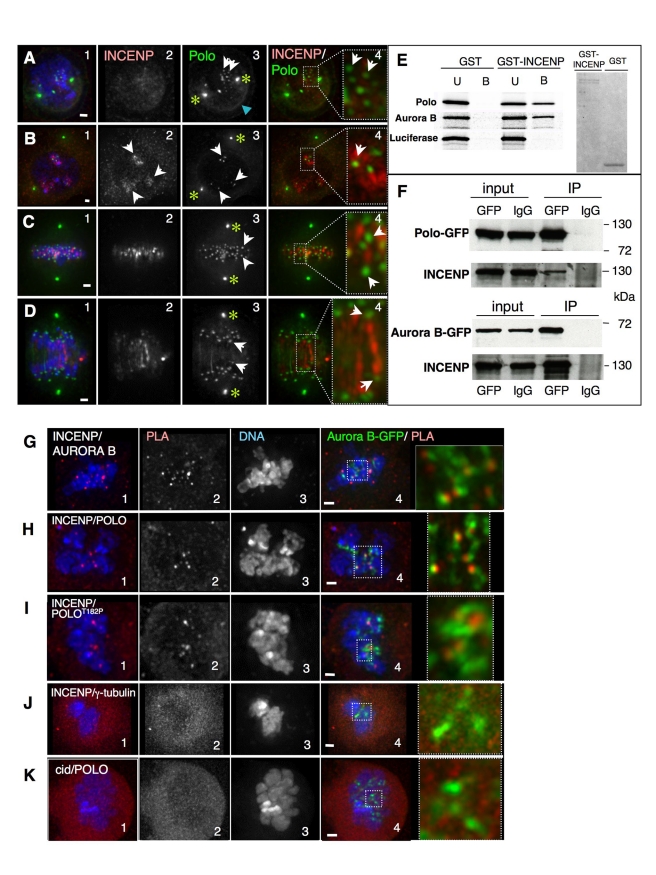
Figure 1. INCENP colocalizes with Polo in early mitosis and interacts with Polo at the inner centromere.
(A) Early prophase, Polo is localized at centrosomes (asterisks), nuclear envelope (blue arrowhead), and starts appearing on chromosomes (white arrows), while INCENP is not yet clearly associated with chromatin. (B) Late prophase, INCENP appears associated with heterochromatin but not yet concentrated at the inner centromere (2, arrows), while Polo is already concentrated in dots colocalizing with INCENP-positive regions (3, white arrows). (C) Metaphase, INCENP at the inner centromere region stretching between Polo-positive kinetochores (arrows). (D) Early anaphase, INCENP decorates thread-like structures joining the segregating Polo-positive sister kinetochores (arrows). Green, Polo-GFP; red, INCENP. Scale bar = 1 µm. (E) In vitro pulldown assays. GST or GST-tagged INCENP were incubated with in vitro translated 35S labelled Polo, Aurora B, or Luciferase. U, unbound fraction; B, bound fraction. Right panel, Coomasie stained gel showing the proteins used for the pulldown. (F) Immunoprecipitation assays. Protein extracts from Polo-GFP (upper panel) or Aurora B-GFP (lower panel) stably transfected cell lines were used in IP experiments using anti-GFP or IgG (Input, whole cell extract, 1% of total loaded; IP, bound fraction, 20% of total loaded). (G–K) Proximity ligation assay (PLA) using antibodies against (G) INCENP and Aurora B (positive control); (H) INCENP and Polo; (I) INCENP and PoloT182Ph; (J) INCENP and γTubulin (negative control); and (K) Polo and CID (Negative control). Zoomed panels show colocalization of the PLA signal (red) with Aurora B-GFP. Scale bar = 1 µm.