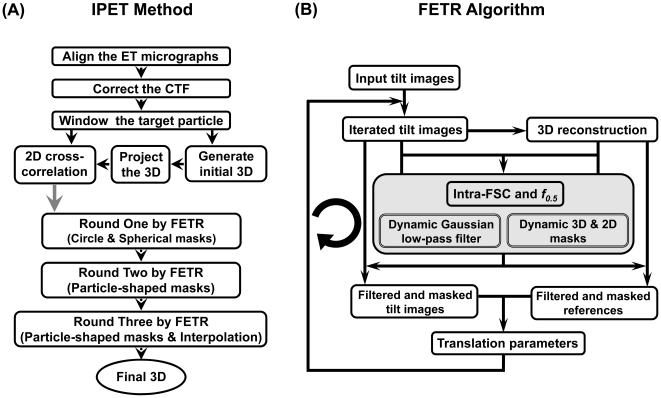
Figure 2. Flow diagram of individual-particle electron tomography (IPET) method and focused electron tomography reconstruction (FETR) algorithm.
(A) The IPET method contains two phases: the electron tomography (ET) data collection with image preprocessing, and a focused electron tomography reconstruction (FETR) algorithm. In the first phase, the single-instance of particle was imaged by ET. The contrast transfer function (CTF) of the whole-micrograph-size tilt images was determined, and then corrected after tilt images were aligned. The small images containing only a targeted particle were selected and windowed from each of tilt whole-micrograph, and then directly back-projected into 3D as the initial/starting model for refinement. The 3D reconstruction refinement procedure contains three rounds of refinement loops in the FETR algorithm. Each round was essentially the same, except different masks were applied. In the first round, a series of automatically generated circular Gaussian-edge masks was used; in the second round, the automatically generated particle-shaped masks were used and while, in the third round, the last mask in second round was used with association of an additional interpolation method during determining the translation parameters. (B) Each round of refinement loops contains the same iteration algorithm, FETR. 3D reconstruction from the previous iteration (or initial model for the first iteration) was projected, and the projections were used as references for the next iteration. Before translational parameter searching, a dynamic Gaussian low-pass filter and automatically generated mask were applied to both the references and tilt images.