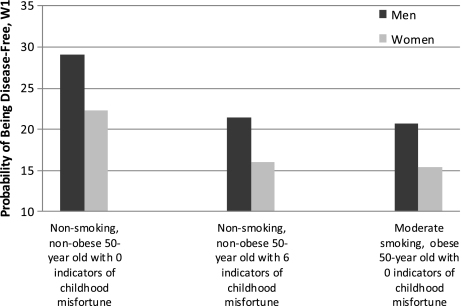
Figure 1.
Comparison of childhood misfortune with other important risk factors for the predicted probability of disease avoidance. Note: Probabilities are calculated from the multivariate logistic regression model presented in Table 1. Besides childhood misfortune, smoking, obesity, age, and gender, all control variables are held at their means. Moderate smoking is defined as the 25th percentile lifetime smoking value for people who have ever smoked in the sample (equivalent to nearly 66,000 lifetime cigarettes; 65% of MIDUS respondents within that approximate value were former smokers in the 1995 interview).