Fig. 1.
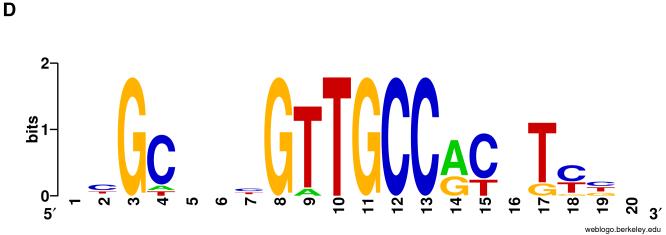
A Silencer Element (SE) + Downstream Element (DE) cis-regulatory motif combination is a shared feature of insect brk genes. A: Annotated scale diagrams of the brk gene and its upstream non-coding sequences in representatives of various insect orders. Blue boxes represent brk protein coding sequences; white boxes represent untranslated regions. Arrows denote direction of transcription and are positioned at either the transcription start site or the start codon of the gene. Except in the case of Ag and Aa, the entire intergenic region between brk and the next upstream gene is shown. Dpp Silencer Elements (Yao et al., 2008) are indicated by “S”; Downstream Elements are denoted by “D”. Shared S+D motif combinations are shown in red. Lower-case “s” upstream of Rp brk denotes single-base mismatch to the S motif definition; lower-case “d” upstream of Ag, Nv, and Ap brk denotes single-base mismatch to the D motif definition (see C for alignment). Other single-base mismatches to either motif are omitted. Sequence scale indicated in upper right corner. Dm, Drosophila melanogaster (Diptera); Ag, Anopheles gambiae (Diptera); Aa, Aedes aegypti (Diptera); Bm, Bombyx mori (Lepidoptera); Tc, Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera); Am, Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera); Nv, Nasonia vitripennis (Hymenoptera); Ap, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Hemiptera); Rp, Rhodnius prolixus (Hemiptera). B: Logo plots of the “special” SE subset (upper, 10 occurrences) and all “other” SE motifs (lower, 32 occurrences) upstream of the insect brk genes shown in A. Note the additional sequence constraint in the “special” subset in both unconstrained (5, 8, 10, 12-14) and partially degenerate (7) positions within the motif, as well as in flanking positions (3, 20, 21), compared to that in the “other” set. The “special” subset has an uncorrected sequence information content of 30.35 bits, far higher than the mean of 21.01 bits for 1000 randomly chosen sets of 10 SE motif instances drawn from the non-coding portion of the fly genome (see Materials and methods). By contrast, the “other” subset has an uncorrected sequence information content of 20.43 bits, compared to a mean of 18.62 bits for 1000 randomly chosen sets of 32 SE motif instances. C: Sequence alignment of the SE+DE motif combinations shown in red in A. Except for the two occurrences in Ag, actual distances between SEs and the corresponding DEs are shown. D: Logo plot of the DE motifs associated with the 10 “special” SEs (see A, C).